What sizes do PVC ball valves come in?
PVC ball valves offer a wide array of sizes. Common applications typically utilize valves ranging from 1/4 inch up to 4 inches. Specialized industrial requirements often call for larger options, which extend to 12 inches. Manufacturers produce these PVC ball valves to meet diverse fluid control needs across various systems.
Key Takeaways
- PVC ball valves come in many sizes, from small 1/4 inch valves for homes to large 12 inch valves for big factories.
- Choosing the right size valve is important. Match it to your pipe, how much water you need to flow, and the water pressure.
- Larger valves handle more water and are used in bigger systems like irrigation or industrial settings.
Common Small PVC Ball Valve Sizes
Manufacturers produce a range of small PVC ball valves for precise flow control in various systems. These smaller sizes are essential for applications requiring compact components and accurate regulation.
1/4 Inch PVC Ball Valves
The 1/4 inch PVC ball valve represents one of the smallest available options. These valves are frequently utilized in aquariums, water lines, and chemical processing. They also provide a cost-effective solution for budget-sensitive projects. Irrigation systems benefit from their lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. A 1/4 inch in-line check valve, a specific type of small PVC valve, prevents suds from siphoning back into the buffer tank in soap tank setups.
3/8 Inch PVC Ball Valves
Slightly larger than the 1/4 inch, 3/8 inch PVC ball valves offer increased flow capacity while maintaining a compact footprint. Users often select these valves for similar small-scale applications where a marginally higher volume of fluid movement is necessary. They fit well into tight spaces and provide reliable shut-off capabilities.
1/2 Inch PVC Ball Valves
The 1/2 inch PVC ball valve is a very common size for residential and light commercial plumbing. A B&K 1/2 inch PVC slip ball valve, model 107-603, for example, carries a rating for a maximum pressure of 150 PSI. Generally, PVC ball valves ranging from 1/4 inch to 2 inches are typically pressure-rated for 250 PSI at 70°F under non-shock conditions. Schedule 80 PVC pipes, which are compatible with these valves, have a minimum pressure rating of 200 PSI at 73°F for sizes up to 2 inches.
3/4 Inch PVC Ball Valves
The 3/4 inch PVC ball valve provides a versatile option for many applications. Industries frequently use these valves in industrial settings, water treatment facilities, and pool/spa systems. They are also prevalent in irrigation and commercial plumbing projects, offering robust performance for medium-flow requirements.
Standard Mid-Range PVC Ball Valve Sizes
Mid-range PVC ball valves offer increased flow capacity for a broader spectrum of applications. These sizes balance compact design with robust performance, making them suitable for many residential, commercial, and light industrial systems.
1 Inch PVC Ball Valves
One inch PVC ball valves are a common choice for main water lines in homes and small commercial buildings. They provide efficient flow control for irrigation systems, pool plumbing, and various water treatment processes. Their larger diameter allows for greater fluid volume compared to smaller valves, supporting more demanding flow requirements.
1 1/4 Inch PVC Ball Valves
The 1 1/4 inch PVC ball valve serves applications requiring moderate flow rates. Manufacturers rate certain 1 1/4 inch PVC ball valves for a maximum pressure of 232 PSIG at 73°F. Other models may have a rating of 125 PSI at a static temperature of 72°F. For a 1 1/4 inch Schedule 80 PVC ball valve, the test pressure is typically 225 psi at 73°F, with a working pressure of 150 psi at 73°F. All PVC ball valves from 1/4 inch to 2 inches often carry a pressure rating of 250 PSI at 70°F under non-shock conditions.
1 1/2 Inch PVC Ball Valves
One and a half inch PVC ball valves are notable for their excellent flow characteristics. Their design often includes a standard port, ensuring optimal flow capacity. Many feature a full-port design, which maximizes flow capacity. This configuration reduces pressure loss and enhances system efficiency. A full-port valve matches the inner diameter of the connected pipe, minimizing pressure loss and maximizing flow. A smooth, polished ball surface further reduces friction and turbulence, leading to consistent flow.
2 Inch PVC Ball Valves
Two inch PVC ball valves represent the larger end of the standard mid-range options. These valves are frequently used in larger irrigation mains, industrial fluid transfer, and substantial pool and spa systems. They handle significant flow volumes, making them ideal for applications where high throughput is essential. Their robust construction ensures reliable operation in various demanding environments.
Larger PVC Ball Valve Sizes for Increased Flow
As flow requirements increase, larger PVC ball valve sizes become necessary. These valves handle substantial volumes of fluid, making them suitable for more demanding applications in commercial, industrial, and municipal settings. They ensure efficient operation where high throughput is critical.
2 1/2 Inch PVC Ball Valves
Two and a half inch PVC ball valves bridge the gap between standard mid-range and truly large-scale applications. Users often select these valves for commercial irrigation main lines, larger swimming pool filtration systems, and light industrial processes. They provide a significant increase in flow capacity compared to 2-inch valves, supporting systems that require more robust fluid transfer.
3 Inch PVC Ball Valves
Three inch PVC ball valves are common in industrial water treatment plants, large agricultural irrigation systems, and commercial plumbing mains. Their substantial bore allows for excellent flow rates, minimizing pressure drop across the valve. These valves are crucial for managing large volumes of water or other compatible fluids efficiently. They offer reliable shut-off and flow regulation in demanding environments.
4 Inch PVC Ball Valves
Four inch PVC ball valves represent a significant step up in flow capacity, serving heavy-duty industrial and municipal applications. These valves are essential for main water distribution lines, large-scale chemical processing, and extensive wastewater management systems. Manufacturers design these larger PVC ball valves for durability and performance under considerable flow. For instance, specific series of 4-inch PVC ball valves carry a pressure rating of 235 psi at 70°F under non-shock conditions. This 235 PSI rating applies to sizes ranging from 2-1/2 inches to 4 inches, indicating their robust construction for higher pressure demands.
Specialized and Industrial PVC Ball Valve Sizes
For applications demanding extremely high flow rates and robust control, manufacturers offer specialized and industrial-grade PVC ball valves in significantly larger dimensions. These valves cater to heavy-duty requirements beyond typical commercial or residential use.
6 Inch PVC Ball Valves
Six-inch PVC ball valves find their place in major industrial pipelines, large-scale water distribution networks, and extensive chemical processing facilities. Their substantial diameter allows for the efficient movement of vast fluid volumes, minimizing pressure loss across the system. These valves are critical for managing flow in large infrastructure projects.
8 Inch PVC Ball Valves
Eight-inch PVC ball valves are essential for very large-scale fluid handling. Industries use them in municipal water treatment plants, large irrigation main lines, and significant industrial waste management systems. They provide reliable shut-off and flow regulation for critical processes where high capacity is non-negotiable.
10 Inch and 12 Inch PVC Ball Valves
The largest standard sizes for PVC ball valves typically extend to 10 inches and 12 inches. These massive valves are crucial for the most demanding industrial and municipal applications. For instance, standard offerings include 4-inch NPT PVC ball valves, alongside industrial versions in 2-inch, 3-inch, and 4-inch sizes. However, specialized manufacturers produce even larger options like 10-inch and 12-inch valves to handle extreme flow requirements in major infrastructure projects.
Custom PVC Ball Valve Options
When standard sizes do not meet specific project needs, custom PVC ball valve options become available. Manufacturers can design and produce valves tailored to unique specifications, including non-standard dimensions, specialized end connections, or particular pressure ratings. Customers should plan for lead times when ordering custom valves. The average lead time for such orders is typically around 4 weeks, with some products having lead times of 30 days.
Specific Types of PVC Ball Valves and Their Sizes
Beyond the general size categories, specific types of PVC ball valves cater to unique installation and operational requirements. These specialized designs often come in particular size ranges to optimize their intended function.
Compact PVC Ball Valves Size Range
Compact PVC ball valves provide effective flow control in applications with limited space. Manufacturers produce these valves in a broad size range, typically from ½-inch up to 6-inch. For common IPS sizes between 1/2″ and 4″, customers can find options with socket, threaded, or flanged end connectors. The larger 6-inch compact valve usually comes with either socket or flanged end connections. Specialized compact valves also exist for specific uses. For example, a 1/4 inch PVC Labcock Ball Valve offers precise regulation for laboratory settings. Another notable option is the 3/8″ Asahi Type-27 Omni® Ball Valve, which is available in sizes from 3/8″ to 2″ and features socket or threaded end connections. A 1″ White PVC Compact Ball Valve is a widely used model, balancing a small footprint with adequate flow capacity. These valves are ideal for systems where space is a premium but reliable shut-off is still essential.
PVC True Union Ball Valves Size Availability
PVC true union ball valves offer significant advantages in terms of installation and maintenance. Their unique two-piece body design allows technicians to easily remove the valve from a pipeline without disassembling the entire system. This feature simplifies repairs and replacements. Common sizes for these highly versatile valves include the 1-inch true union ball valve, which is popular for many residential and commercial uses. The 1-1/2 inch PVC true union ball valve provides increased flow capacity for more demanding applications. Manufacturers typically offer these valves in sizes up to 2 inches, providing both socket and threaded end connections to accommodate diverse piping configurations. Their robust construction and convenient design make them a preferred choice across various industrial, agricultural, and commercial fluid handling systems.
Key Factors for Selecting PVC Ball Valve Sizes
Selecting the correct size for a valve is critical for optimal system performance. Several factors influence this decision, including pipe diameter, required flow rate, pressure considerations, and specific application needs. Careful evaluation of these elements ensures efficient operation and system longevity.
Matching Pipe Diameter for PVC Ball Valves
Matching the valve size to the pipe’s diameter is a fundamental step in valve selection. Neglecting to match the valve to the pipe diameter and required flow rate is a common mistake. The selection of a ball valve must align with the pipe’s diameter and the system’s flow rate to ensure efficient operation and prevent excessive pressure drops. For applications demanding high efficiency and minimal pressure drop, full-bore valves are preferable. Full-port valves, with a bore size matching the pipe diameter, offer minimal flow restriction and maximize flow capacity. In contrast, reduced-port valves have a smaller opening, which can impact flow capacity but may offer cost savings. Proper sizing, considering fluid properties, piping layout, and operating conditions, helps mitigate pressure losses and maintain system efficiency.
Flow Rate Requirements for PVC Ball Valves
Flow rate is a primary consideration when choosing valve sizes. Ball valve sizing is crucial for minimizing pressure drop and maintaining consistent flow rates. Full-port valves, with a bore size matching the pipe diameter, offer minimal flow restriction and maximize flow capacity. Engineers often use the valve flow coefficient (Cv) to quantify a valve’s flow capacity. This coefficient represents the volume of water (in US gallons per minute) at 60°F that flows through a valve with a pressure drop of 1 psi.
The equation for calculating the valve flow coefficient (Cv) is: Cv = Q√(SG / ΔP). This formula applies to PVC pipes, as indicated by examples using two-inch inner diameter PVC pipe.
For fluids, the Cv calculation is:
Cv = Q√(SG / (P1 - P2))- Cv = Valve flow coefficient
- Q = Volumetric flow rate (Gallons per minute, GPM)
- P1 = Inlet Pressure (psia)
- P2 = Outlet Pressure (psia)
- SG = Specific Gravity of the fluid
For gases, the Cv calculation varies based on flow conditions:
- Sub-critical flow:
Cv = QG / (1360 * √( (P1 + P2) / (SG * T) )) - Critical flow:
Cv = QG / (836 * √( (P1) / (SG * T) ))- Cv = Valve Flow Coefficient
- QG = Gas Flow in Standard Cubic Feet per Hour
- T = Absolute temperature in °R. (°F + 460)
- P1 = Upstream (inlet) pressure in psia
- P2 = Downstream (outlet) pressure in psia
- SG = Specific Gravity of medium where air at 70°F and 14.7 psia = 1.0
Pressure Considerations for PVC Ball Valves
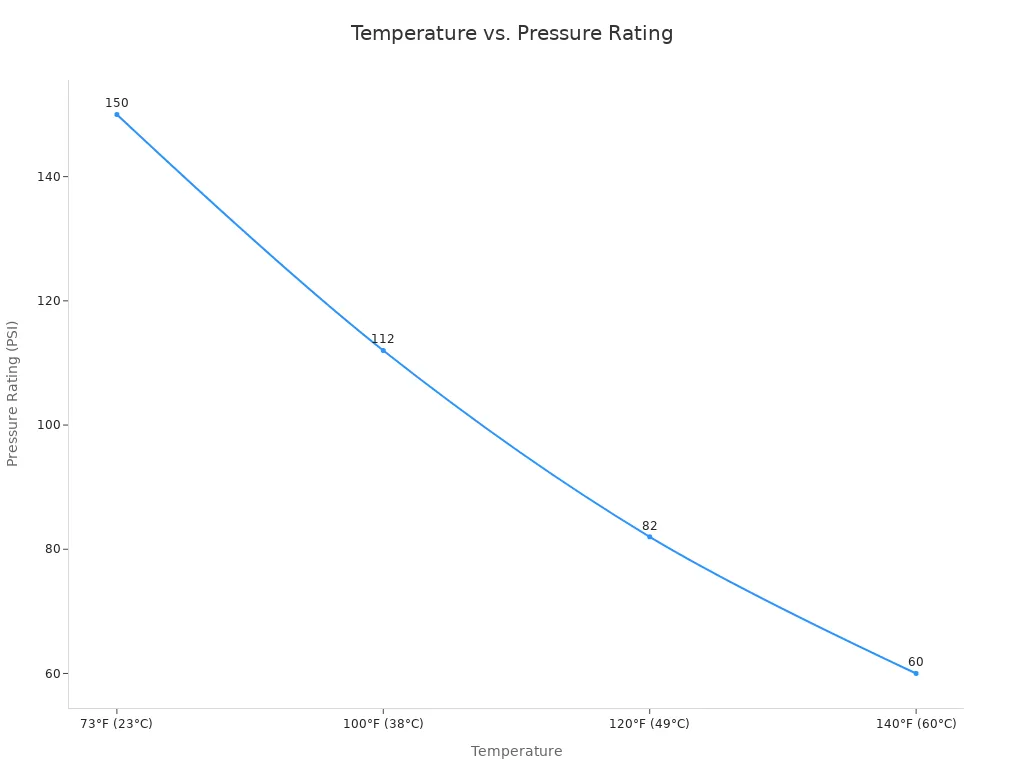
Pressure ratings are vital for safe and reliable operation. Ball valves typically have a maximum pressure rating of 150 PSI. This rating is generally sufficient for common water applications such as irrigation, pools, and residential plumbing. However, temperature significantly impacts a valve’s pressure capacity. As the temperature rises, the strength and rigidity of PVC material diminish, leading to a substantial decrease in its capacity to withstand pressure. This phenomenon is commonly referred to as the ‘pressure de-rating curve,’ and manufacturers typically provide charts detailing these reductions. It is essential to consider these de-ratings for safe and reliable operation of PVC ball valves.
| Temperature (°F/°C) | Pressure Rating (PSI) |
|---|---|
| 73°F (23°C) | 150 |
| 100°F (38°C) | 112 |
| 120°F (49°C) | 82 |
| 140°F (60°C) | 60 |
Application-Specific Needs for PVC Ball Valves
Different applications impose unique requirements on valve sizing. For instance, irrigation systems have specific considerations. A 1 1/2-inch ball valve is frequently installed in irrigation systems. Valve size should be based on the water volume required for a zone, not solely on the mainline or lateral line pipe size. Manufacturers provide pressure loss charts for valves based on flow rate and valve size. The desired pressure loss in a remote control valve ranges from 2 to 5 PSI. Valves for irrigation systems are available in sizes ranging from 1/2″ to 4″. Understanding these application-specific demands ensures the selection of an appropriately sized valve for optimal performance.
PVC ball valves offer a comprehensive range of sizes. They effectively suit diverse plumbing and industrial needs. Proper sizing is crucial for optimal system performance and longevity. Engineers must always consider pipe diameter, flow rate, and pressure when selecting these valve sizes for any application.
FAQ
What is the most common PVC ball valve size for home use?
The 1/2 inch PVC ball valve is very common for residential plumbing. It provides reliable flow control for various household applications.
Does temperature affect PVC ball valve pressure ratings?
Yes, temperature significantly impacts pressure ratings. As temperature increases, PVC material strength decreases, reducing the valve’s capacity to withstand pressure.
Why choose a PVC true union ball valve?
PVC true union ball valves allow easy removal from pipelines. This design simplifies maintenance, repairs, and replacements without disassembling the entire system.