Why Is PPR Compatibility Key for Your PEX and PE Pipe Projects?
Modern plumbing systems demand seamless integration of PPR, PEX, and PE pipes. Proper PPR compatibility directly impacts system reliability and longevity. Achieving optimal PPR compatibility simplifies complex mixed-material installations, offering significant advantages. For instance, using compatible materials like PEX can reduce material costs by 30–50% and speed up installation by 40%. This efficiency is further enhanced with the right PPR FITTING Type2, ensuring a reliable and seamless pipe connection for lasting performance.
Key Takeaways
- PPR compatibility ensures different pipe materials work together. This creates a strong and reliable plumbing system.
- Compatible PPR fittings prevent leaks. They handle temperature changes well and protect against chemical damage.
- Using compatible PPR solutions makes plumbing systems last longer. It also reduces installation time and maintenance costs.
- High-quality, certified PPR products meet strict standards. This ensures safety and good performance.
- PPR systems are easy to install and maintain. They allow for simple changes in the future.
Understanding PPR Compatibility in Mixed Piping Systems
What Defines PPR Compatibility for PEX and PE?
PPR compatibility refers to the ability of polypropylene random copolymer (PPR) fittings and pipes to seamlessly integrate with PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) and PE (polyethylene) piping systems. This integration ensures a unified and functional plumbing network. It involves matching material properties, such as thermal expansion rates and chemical resistance, to prevent stress and degradation at connection points. Achieving proper PPR compatibility guarantees the long-term integrity and performance of mixed-material installations.
The Importance of Material Synergy for Optimal Performance
Material synergy is crucial for optimal plumbing system performance. When different pipe materials and fittings work together harmoniously, the entire system operates efficiently. This synergy prevents common issues like leaks, pressure drops, and premature wear. It ensures consistent water flow and temperature regulation. A well-integrated system, built with synergistic materials, offers enhanced durability and reliability. This approach minimizes maintenance needs and reduces overall operational costs, ultimately extending the lifespan of the plumbing infrastructure.
Common Challenges of Incompatible Connections
Incompatible connections pose significant risks to plumbing systems. They often lead to frequent failure modes. For instance, CPVC pipes commonly experience environmental stress cracking (ESC) when they interact with certain construction materials. These materials include fire caulks, various sealants, duct caulk, and communication cables. Plasticizers in fire caulks can cause ESC, with failures sometimes appearing within three to seven years after installation. Material incompatibility also causes corrosion. Combining different metals, such as brass fittings with unlike materials, can lead to galvanic corrosion. This creates weak points prone to leaks. Additionally, incorrect jointing techniques, like neglecting to seal threaded connections, result in micro-leaks and compromise system strength. These challenges highlight the necessity of selecting compatible components for reliable plumbing.
The Essential Role of PPR Compatibility in Preventing Leaks
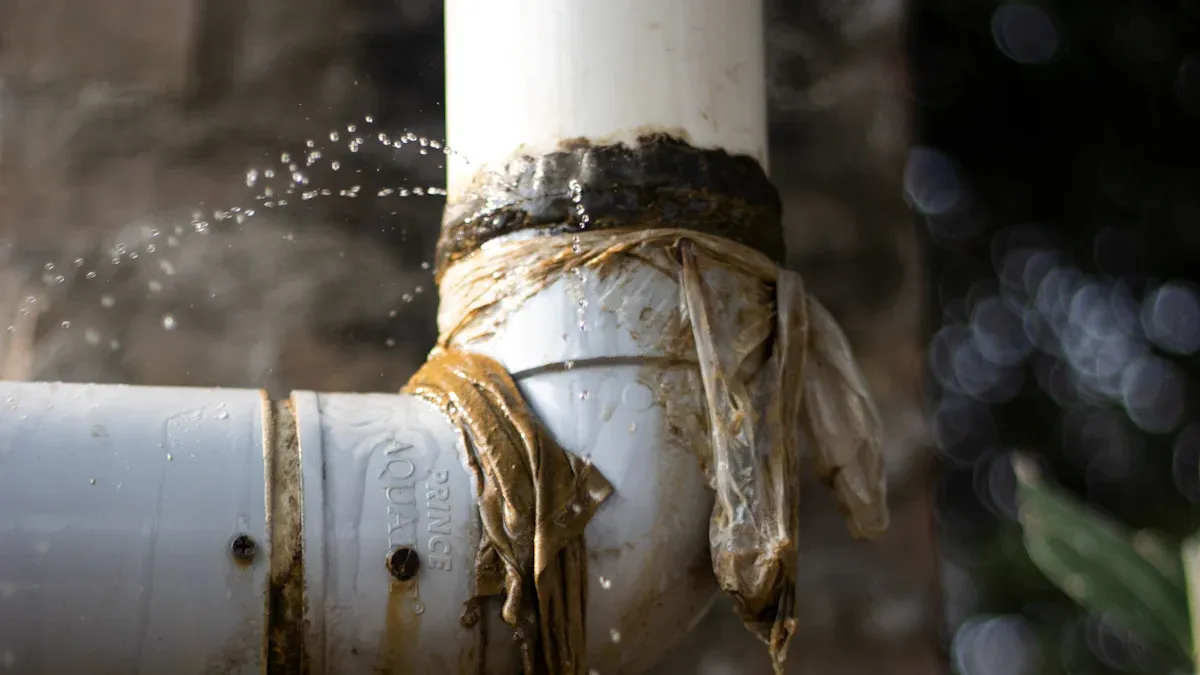

Ensuring Watertight Seals with Compatible Fittings
Achieving watertight seals is fundamental for any reliable plumbing system. Compatible fittings play a critical role in this process. They create a secure, leak-proof connection between different pipe materials. When fittings match the specific properties of PEX, PE, and PPR pipes, they form a strong bond. This bond prevents water from escaping, even under pressure. Using the correct fittings ensures the integrity of the entire system. It eliminates weak points where leaks commonly occur.
Mitigating Thermal Expansion Differences
Pipes expand and contract with temperature changes. Different pipe materials have varying rates of thermal expansion. This difference can stress connections and lead to leaks if not managed properly.
| Pipe Material | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (per ℃) |
|---|---|
| PEX | ~5.5 × 10⁻⁵ |
| PE-RT | ~12 × 10⁻⁵ |
Mechanical connection methods effectively manage these differences. Compression and push-fit fittings are common examples. Compression rings tighten onto the pipe. This creates a pressure-resistant seal. It also allows for slight material expansion variations. Experts advise avoiding rigid connections in high-temperature applications, especially above 60℃ (140℉). This prevents stress from expansion differences. Proper PPR compatibility in these connections is vital for long-term stability.
The Long-Term Benefits of Leak-Proof Systems
Leak-proof systems offer significant long-term benefits. They prevent water damage to buildings and property. Leaks can cause costly repairs, mold growth, and structural issues. A system free from leaks operates more efficiently. It maintains consistent water pressure and flow. This reduces water waste and lowers utility bills. Furthermore, a leak-proof system requires less maintenance. This saves time and money over the lifespan of the plumbing infrastructure. Ensuring PPR compatibility from the start guarantees these advantages.
Enhancing Durability and Longevity Through PPR Compatibility
How Compatible Materials Withstand Stress
Compatible materials in a plumbing system share similar physical properties. This allows them to withstand stress uniformly. When pipes and fittings have matching thermal expansion rates and rigidity, they do not pull apart or create weak points under pressure. This uniform response to stress prevents cracks, fractures, and premature wear. A system built with compatible components distributes mechanical loads effectively. This ensures each part contributes to the overall strength and resilience of the infrastructure.
Protecting Against Chemical Degradation
Chemical degradation poses a significant threat to plumbing systems. Incompatible materials can react with water additives or transported chemicals, leading to corrosion or breakdown. PPR materials offer robust protection against many common chemicals.
- Acids and Alkalis: PPR fittings resist both acidic and alkaline solutions. This makes them suitable for systems transporting fluids with non-neutral pH. They show long-term resistance to low and medium concentrations of common acids and bases.
- Cleaning Agents and Disinfectants: PPR resists common cleaning agents and disinfectants like chlorine-based cleaners and alcohols. This is crucial for environments needing frequent sanitation. It does not absorb or degrade under normal exposure.
- Organic Compounds: PPR performs well with many organic solvents such as esters, ketones, and alcohols. This is useful in laboratories or chemical processing plants for low-risk organic applications.
This inherent chemical resistance safeguards the system’s integrity over time.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Plumbing Infrastructure
Selecting compatible materials significantly extends the lifespan of plumbing infrastructure. When components work together without stress or chemical reactions, they last longer. This reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Proper PPR compatibility ensures the system remains robust against daily wear and environmental factors. A durable system provides consistent performance for many years. This translates into lower long-term costs and greater reliability for property owners.
Streamlining Installation with Compatible PPR Solutions
Reducing Labor and Installation Time
Compatible PPR solutions significantly reduce labor and installation time for plumbing projects. Pipes are lightweight, eliminating the need for heavy lifting equipment. This makes handling and transport much easier. Cutting and welding processes are simple, clean, and safe. Heat fusion technology removes the need for adhesives or mechanical parts. This directly reduces labor time and overall installation costs. Quicker installation speeds up project timelines and decreases man-hours, leading to financial savings for projects.
Simplifying the Connection Process
The connection process becomes remarkably simple with compatible PPR solutions. Installers eliminate the need for glues, sealants, or mechanical connectors. This reduces material purchases and shortens labor time. Installers require fewer tools and less training to complete secure connections. This lowers overall installation costs. Heat fusion joining needs minimal setup. Each joint completes quickly without waiting for adhesives to cure or threading to finish. This accelerates project timelines and lowers on-site labor costs. Fewer work hours mean less money spent on wages and a reduced risk of scheduling delays.
Minimizing the Need for Specialized Tools
Compatible PPR solutions minimize the need for specialized tools. Tools for PPR fusion are generally lightweight and portable. This reduces the need for expensive, specialized equipment. The flexibility of PPR allows cutting and fitting without complex tools. The fusion process ensures strong joints without excessive equipment. The straightforward assembly method is quickly learned and consistently applied. This is valuable for large-scale projects or situations where skilled labor is limited. This ease of installation and adaptability makes PPR compatibility excellent for retrofits. It reduces time and labor for system updates during renovations.
Practical Considerations for Selecting Compatible PPR Fittings

Selecting the correct PPR fittings is crucial for any PEX and PE pipe project. Careful consideration ensures the long-term success and reliability of the plumbing system. Installers must evaluate product quality, understand fitting types, and confirm adherence to industry standards. This proactive approach prevents future complications and guarantees optimal performance.
Identifying High-Quality, Certified Compatible Products
Identifying high-quality, certified compatible products is essential for durable plumbing systems. Manufacturers must ensure their PPR products meet stringent quality and performance criteria. These certifications provide assurance of reliability and safety.
- International Standards: Several international standards define the quality and performance of PPR piping systems. These include ISO 15874, DIN 8078, ASTM F2389, and EN ISO 21003. They specify mechanical properties, pressure ratings, and testing protocols. ISO 15874, for example, is the primary global standard for PPR systems. It outlines requirements for hot and cold water installations, including dimensions, pressure ratings, test methods, and jointing techniques. Compliance ensures fittings withstand continuous use at 70°C and surges up to 95°C.
- European Standards: In Europe, DIN 8077/8078 and EN ISO 15874 regulate material properties, dimensional tolerances, and wall thickness for consistency.
- National Standards (US): ASTM F2389 serves as the primary standard for pressure-rated polypropylene (PP) piping systems in the United States. It covers materials, dimensions, and performance.
- National Standards (UK): BS 6920 evaluates the suitability of non-metallic materials for use with potable water in the United Kingdom.
- Certification Bodies: Reputable certification bodies verify product compliance. WRAS (Water Regulations Advisory Scheme) certifies UK plumbing products, ensuring compliance with water supply regulations and non-contamination. NSF (National Sanitation Foundation) certification (NSF/ANSI 14 and NSF/ANSI 61) is vital for drinking water systems in North America. It tests for health effects and performance. For potable water, certifications like NSF/ANSI 61 (North America), WRAS (UK), and ACS (France) ensure no harmful chemicals leach into drinking water. Manufacturers must also ensure production processes are free of heavy metals, plasticizers, and toxic additives. Fittings are tested for biofilm resistance.
- Quality Management Certifications: ISO 9001 demonstrates a manufacturer’s commitment to high-quality production through its quality management systems. ISO 14001 indicates a commitment to minimizing environmental impact through environmental management systems.
Choosing products from manufacturers like DONSEN, established in 1996, ensures access to products that meet these rigorous standards. DONSEN adopts imported high-quality raw materials and advanced production lines. They have passed CE certification for the European Union, NSF certification in the USA, SABS certification in South Africa, GOST certification in Russia, WRAS certification in England, SIAA certification in Japan, and Germany’s SKZ certification. This extensive certification portfolio highlights their dedication to product quality and compatibility.
Understanding Different Types of Transition Fittings
Transition fittings bridge the gap between different piping materials. They are essential when connecting PPR to PEX or PE pipes. Each type offers specific advantages for various applications.
- Mechanical Transition Fittings: These fittings use compression or crimping mechanisms to create a seal. They do not require heat or special bonding agents. Installers often use them for PEX connections. They provide flexibility during installation and allow for disassembly if needed.
- Threaded Adapters: Threaded adapters connect PPR pipes to PEX or PE pipes that have threaded ends. These adapters typically feature a PPR end for fusion and a metal or plastic threaded end for connection. Installers must use appropriate sealants or tape to ensure a watertight seal.
- Fusion Transition Fittings: These fittings are specifically designed for heat fusion. They create a homogeneous bond between PPR and other compatible plastic pipes. This method results in a very strong, leak-proof connection. It is often preferred for permanent installations.
- Push-Fit Fittings: Some systems utilize push-fit fittings for quick and easy connections. These fittings simply push onto the pipe, creating a secure seal. They are convenient for repairs or modifications but may not be suitable for all high-pressure applications.
Selecting the correct transition fitting depends on the specific pipe materials, system pressure, and installation environment. Installers must ensure the chosen fitting is explicitly designed for compatibility with both PPR and the other pipe material.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is non-negotiable for any plumbing project. These guidelines ensure safety, performance, and environmental responsibility.
- Quality Standards:
- Material Standards: PPR pipes must conform to international standards like ISO 15874. This standard specifies physical, mechanical, and chemical properties.
- Manufacturing Standards: Manufacturers must adhere to standards such as ISO 9001. This ensures consistent processes and product quality.
- Product Standards:
- Dimensional Standards: PPR pipes must conform to dimensional standards like DIN 8077/8078. These standards define specific dimensions and tolerances.
- Pressure Rating Standards: Standards such as ASTM F2389 specify pressure ratings for PPR pipes. This ensures they can withstand operating conditions.
- Safety Regulations: PPR pipes must comply with health and safety regulations. These include limits on hazardous substances. They also must meet fire safety regulations, such as those concerning flame retardancy and smoke generation.
- Application-Specific Standards:
- ISO 15874: This standard specifically addresses PP-R piping systems for hot and cold water installations. It does not mention compressed air applications.
- ASTM F2389: This standard governs polypropylene pressure pipes for water service only.
- ISO 10380: This standard covers gas installation systems. It typically focuses on metallic or specially engineered piping. It excludes standard PPR materials.
- ASME B31.3: This provides guidelines for industrial piping systems, including compressed air. It generally requires materials with proven performance in gas service, which standard PPR cannot meet.
Adhering to these standards protects the end-user and ensures the longevity of the plumbing system. DONSEN’s products, widely used in civil water supply, building drainage, water supply and heating, home decoration, and garden irrigation, demonstrate compliance with these diverse international standards. Their global presence in over 100 countries, including Russia, Ukraine, France, Italy, and Mexico, underscores their commitment to meeting varied regional and international regulations.
PPR Compatibility Versus Alternative Connection Methods
Performance and Reliability Comparison
PPR compatible connections offer superior performance compared to many alternative methods. They maintain consistent operation across a wide temperature range. For example, PPR fittings perform well from 20°F to 180°F. They also sustain pressure ratings up to 174 psi at 176°F. This is much higher than PVC alternatives. PPR also shows impact strength down to -4°F. It has fatigue resistance exceeding 50 million pressure cycles. Industrial versions can handle constant operating pressures over 200 psi. This is due to specialized fiber reinforcement.
| Brand | Pressure Rating (psi) | Temperature Range (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| AquaPipe Pro | 185 @ 73°F, 152 @ 140°F | 14°F to 194°F |
| FlowTech HD | 175 @ 73°F, 140 @ 140°F | 23°F to 185°F |
| HydroSafe Elite | 192 @ 73°F, 162 @ 140°F | -4°F to 203°F |
PPR’s smooth interior surfaces also improve flow efficiency. They have a Hazen-Williams coefficient of 150. Copper’s coefficient is 130. This leads to an approximate 8% reduction in pump energy needs. PPR also has a lower expansion coefficient (0.15 mm/m°C) compared to HDPE (0.20 mm/m°C). This means less stress from thermal changes.
Cost-Effectiveness Over the System’s Lifespan
PPR systems prove more economical over their lifespan compared to traditional materials. This includes copper and PVC. They offer superior durability and chemical resistance. This leads to a longer lifespan.
- Material Costs: PPR fittings might have higher initial costs. However, they offer superior durability. They resist corrosion, scaling, and chemical degradation. This reduces the need for frequent replacements. This is especially true in harsh environments.
- Labor Costs: PPR systems are easy to install. They only require a heat fusion tool and basic training. This reduces labor time and costs. Their lightweight nature also simplifies handling.
- Maintenance Costs: PPR systems resist corrosion, scaling, and chemical degradation. This leads to low maintenance needs. It also reduces repair frequency. They can last over 50 years with minimal intervention.
- Energy Efficiency: Smooth inner walls minimize friction. This improves flow efficiency. It lowers pumping costs. Superior thermal insulation properties reduce energy loss during fluid transfer.
Commercial-grade PP-R systems offer exceptional durability. They have a lifespan exceeding 50 years. This makes them a long-term investment.
Ease of Maintenance and Future Modifications
PPR compatibility simplifies maintenance and future modifications. PPR pipes resist corrosion and extreme temperatures. This reduces maintenance needs. Their lightweight design simplifies installation. This also reduces labor costs and project completion times. Seamless heat-fused joints ensure leak-proof connections and reliability. These joints are permanent. They do not require tightening or sealing over time. This reduces the need for routine checks. Modifying a PPR system is also straightforward. Installers can easily cut and re-fuse sections. This allows for system expansions or changes without extensive rework. This adaptability makes PPR an excellent choice for evolving plumbing needs.
Best Practices for Achieving Optimal PPR Compatibility
Achieving optimal PPR compatibility requires careful planning and precise execution. Following best practices ensures secure, long-lasting connections in mixed-material plumbing systems. These practices cover everything from initial preparation to final inspection.
Step-by-Step Guide for Secure Connections
Creating secure connections between PPR, PEX, and PE pipes involves specific methods for each material. Installers must follow these steps carefully.
General connection methods apply to various plastic water pipes, including HDPE and PEX:
- Mechanical Fittings (Compression / Threaded): These work for PVC, HDPE, and PPR.
- Insert the pipe into the fitting body. It may or may not have rubber sealing rings.
- Tighten the compression nut or threaded section.
- Test for leaks after complete installation.
- Electrofusion: This method is for HDPE pipes.
- Clean and align the pipe ends within the fitting.
- Apply voltage through the fitting’s embedded wires.
- Allow the melt and fusion to cool.
- Butt Fusion: This method is also for HDPE pipes.
- Heat the pipe ends using a hot plate.
- Press the heated ends together under controlled pressure.
- Allow them to cool to form a continuous pipe.
- Push-Fit / Snap-On Fittings: These are for PEX and light-duty systems.
- Cut the pipe to the desired length.
- Insert the pipe directly into the fitting until it clicks.
- Verify secure engagement. Check indicator rings if they are present.
A general installation guide applies to most plastic pipes:
- Prepare Tools: Gather a pipe cutter, deburring tool, glue or fusion machine, and measuring tape.
- Cut and Clean: Always cut pipes squarely. Thoroughly clean all contact areas.
- Attach Fittings: Use the correct fitting for the chosen connection method. Examples include solvent weld or threaded.
- Align and Join: Ensure the pipe is fully seated and properly aligned within the fitting.
- Pressure Test: Conduct a pressure or leak test before concealing or burying the system.
PEX pipes have several specific connection methods:
- Crimping Method:
- Slide a copper crimp ring over the PEX pipe end.
- Insert the pipe into the PEX fitting.
- Position the crimp ring approximately 1/8 inch from the fitting’s edge.
- Use a crimping tool to compress the ring. This secures the pipe to the fitting.
- Verify the tightness and security of the crimp. Use a crimp gauge for confirmation.
- Clamping Method:
- Slide a stainless steel clamp over the PEX pipe end.
- Insert the PEX pipe into the fitting.
- Position the clamp to cover the pipe and fitting junction.
- Use a clamp tool to tighten the clamp firmly. Ensure no gaps remain.
- Push-Fit Method:
- Insert the PEX pipe end into the push-fit fitting.
- Push until the pipe is fully inserted. The internal locking mechanism engages.
- Gently pull the pipe to confirm it is securely locked.
- Expansion Method (for PEX-A pipes):
- Use an expansion tool to enlarge the end of the PEX-A pipe.
- Insert the expansion fitting into the expanded pipe.
- Allow the pipe to contract back to its original size. This secures the fitting.
- Check for any leaks or movement in the connection.
For PPR fitting installation, follow these steps:
- Preparation and Planning: Assess the installation site. Plan the piping layout. Gather all necessary tools, including PPR fittings, pipes, a cutter, a deburring tool, and welding equipment. Review manufacturer guidelines for compatibility and instructions. Ensure accurate measurements.
- Cutting and Deburring Pipes: Use a pipe cutter to make straight, clean cuts to the required length. Deburr pipe ends to remove rough edges. This prevents damage to the fitting’s sealing surface. It also ensures a smooth connection.
- Fitting and Alignment: Fit PPR fittings onto pipes. Ensure proper alignment and full insertion. For welded fittings, such as socket fusion, clean surfaces. Heat the pipe and fitting to recommended temperatures. Join them according to manufacturer guidelines for a strong bond.
- Testing the System: After installation and cooling, if welded, gradually pressurize the system. Inspect all joints for leaks. Conduct a pressure test as per manufacturer specifications. Address any detected leaks promptly.
- Final Inspection and Maintenance: Perform a final check for secure, aligned fittings and any damage. Implement regular maintenance. This includes periodic inspections and cleaning. This ensures long-term reliability.
Essential Tools and Techniques for Installation
Proper tools and techniques are vital for ensuring optimal PPR compatibility during installation. They guarantee strong, leak-proof connections.
Essential tools include:
- Fusion welding machines
- Pipe cutters
- Deburring tools
- Measuring instruments
Installation techniques involve:
- Correct Fusion Welding Equipment: Use proper fusion tools with temperature control. Ensure precise alignment and timing according to pipe diameter. Failure to follow fusion protocols can lead to leaks or joint failure. Always consult the manufacturer’s welding guidelines.
- Precise Measurement, Cutting, and Alignment: Make clean, straight cuts using a sharp pipe cutter. Clean pipe ends thoroughly before welding. Ensure proper insertion depth during fusion. Incomplete fusion or contamination at joints can create weak spots and system failure.
- Socket fusion welding: This is a common technique.
- Adherence to proper heating time, pressure application, and cooling duration: Base these on manufacturer guidelines.
- Precise alignment and cleanliness of pipe ends: These are crucial for a strong bond.
- Post-installation pressure testing: This confirms the integrity of the system.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Mixed-Material Systems
Even with careful installation, issues can arise in mixed-material plumbing systems. Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems helps maintain system integrity.
- Leaks at Connection Points: Leaks are the most frequent problem. They often result from improper installation or incompatible materials. Check if the correct transition fittings were used. Ensure all connections are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. For fusion joints, inspect for incomplete fusion or cold spots. Re-fuse or replace faulty sections.
- Material Degradation: Incompatible materials can degrade over time. This leads to cracking or weakening. Look for signs of discoloration, brittleness, or swelling near connection points. This indicates a chemical reaction or stress. Replace degraded sections with compatible materials. Ensure proper chemical resistance for the transported fluids.
- Thermal Expansion Stress: Different materials expand and contract at varying rates with temperature changes. This can stress rigid connections. Look for cracks or separations at joints, especially in systems with hot water. Use flexible transition fittings or expansion loops where significant temperature fluctuations occur. This accommodates movement.
- Reduced Flow or Pressure: Blockages or internal scaling can reduce water flow. While PPR resists scaling, incompatible materials might not. Inspect the interior of pipes and fittings for buildup. Ensure all pipe diameters are appropriate for the required flow rate.
- Connection Failures: A connection might fail completely. This often happens due to excessive stress, poor installation, or material fatigue. Identify the cause of the failure. Replace the entire connection with properly installed, compatible components.
Regular inspections and adherence to manufacturer guidelines prevent many of these issues. When troubleshooting, always prioritize safety. Turn off water supply before attempting repairs.
PPR compatibility is critical for successful PEX and PE pipe projects. It ensures the creation of unified, durable, and leak-proof plumbing systems. These systems offer long-term reliability. Adopting compatible PPR solutions guarantees future-proof and efficient installations. This approach minimizes maintenance and maximizes performance for any project.
FAQ
What does PPR compatibility mean for plumbing systems?
PPR compatibility ensures PPR pipes and fittings integrate seamlessly with PEX and PE systems. This creates a unified, functional plumbing network. It matches material properties like thermal expansion and chemical resistance. This prevents stress and degradation at connection points.
How does PPR compatibility help prevent leaks?
Compatible PPR fittings create secure, watertight seals between different pipe materials. They also mitigate thermal expansion differences. This prevents stress on connections. A leak-proof system avoids water damage and operates efficiently.
What are the long-term advantages of using compatible PPR solutions?
Compatible PPR solutions enhance durability and longevity. They withstand stress and protect against chemical degradation. This extends the plumbing infrastructure’s lifespan. They also streamline installation, reducing labor and maintenance costs over time.
Does DONSEN offer certified compatible PPR products?
Yes, DONSEN provides high-quality, certified compatible PPR products. They meet international standards like CE, NSF, SABS, GOST, WRAS, SIAA, and SKZ. DONSEN uses imported raw materials and advanced production lines. This ensures product quality and broad compatibility.
Is PPR easy to install with other pipe types?
Yes, compatible PPR solutions simplify installation. They reduce labor and installation time. The connection process is straightforward. It minimizes the need for specialized tools. This makes PPR an efficient choice for mixed-material projects.
See Also
Air Fryer Perfection: Crispy McCain Craft Beer Fries Every Time