Which PPR Pipe Fittings Guarantee a Durable Water Supply System?

High-quality PPR Pipe fittings form the cornerstone of a resilient and long-lasting water supply system. Superior PPR Pipe material and precise manufacturing ensure system integrity for decades. These inherent advantages prevent leaks and guarantee reliability. Understanding which specific PPR Pipe fittings offer the best performance is crucial for any durable plumbing infrastructure.
Key Takeaways
- High-quality PPR pipe fittings use pure materials. They resist corrosion and chemicals. This makes them last a long time.
- Good PPR fittings follow strict rules. They have certifications. This ensures they are safe and work well.
- PPR pipes need the right wall thickness. This helps them handle water pressure. It stops leaks and breaks.
- Proper heat fusion makes strong pipe joints. This stops leaks. It makes the water system last longer.
- Regular checks and good care keep PPR pipe systems working well. This helps avoid damage. It makes the system last many years.
Key Characteristics of Durable PPR Pipe Fittings

Selecting the right PPR pipe fittings requires understanding their fundamental characteristics. These features directly influence the longevity and reliability of a water supply system.
Material Purity and Grade for PPR Pipe Longevity
The foundation of a durable PPR pipe fitting lies in its raw material. Manufacturers use 100% Type-3 random copolymer polypropylene (PP-R 80 or PP-RCT) for high-grade fittings. This material ensures high molecular integrity, providing superior resistance to both pressure and heat. Such quality contributes to a service life extending up to 50 years.
High-grade PPR offers several critical advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: Unlike metal pipes, PPR fittings do not corrode. This maintains their structural integrity over decades.
- Chemical Resistance: They withstand a wide array of chemicals, preventing degradation from harsh substances. This property significantly contributes to long-term durability.
- Smooth Interior Surface: The smooth inner walls minimize friction and prevent scale buildup. This ensures consistent water flow and extends the pipe’s life by reducing clogs.
- High-Temperature Resistance: PPR fittings can safely handle hot water up to 95°C (203°F) without deterioration. This feature is crucial for many plumbing systems.
- Non-Toxic and Hygienic: PPR is non-toxic, guaranteeing safe drinking water. It also resists bacterial growth, maintaining water purity.
- Thermal Stability and Mechanical Strength: The material exhibits excellent thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity in hot water systems. Its high tensile strength and flexibility allow PPR fittings to endure significant stresses and resist cracking.
Adherence to Manufacturing Standards and Certifications
Reliable PPR pipe fittings strictly adhere to international manufacturing standards and hold relevant certifications. These benchmarks ensure consistent quality, safety, and performance.
Key international standards include:
- ISO 15874: This primary global standard specifies requirements for PPR systems in hot and cold water installations. It covers dimensions, pressure ratings, test methods, and jointing techniques. This standard ensures fittings can withstand continuous use at 70°C and surges up to 95°C.
- DIN 8077/8078 and EN ISO 15874: These European standards regulate material properties, dimensional tolerances, and wall thickness. They ensure consistency across production batches, especially for public infrastructure and certified green buildings.
These standards dictate several critical aspects of manufacturing:
- Raw Material Selection: Standards mandate the use of virgin polypropylene random copolymer (Type 3 or PP-R) with specific melt flow rates and resistance properties.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Strict dimensional tolerances for diameters, wall thickness, and curvature ensure tight fits and secure welds.
- Thermal Stability and Pressure Testing: Manufacturers conduct hydrostatic pressure tests at elevated temperatures (e.g., 1.6 MPa at 95°C for 1,000 hours). This verifies fittings maintain integrity under real-world conditions.
- Joint Integrity: Standards require uniform melting behavior for complete bonding during socket fusion welding.
- Mechanical Strength: Requirements for impact resistance and tensile strength ensure durability against mechanical stress.
- Environmental and Hygiene Standards: For potable water, standards ensure fittings do not leach harmful chemicals, remain free of heavy metals, and resist biofilm formation.
Certifications further validate product quality and safety:
- NSF/ANSI 61, WRAS, and ACS: These national certifications are crucial for potable water systems. They ensure fittings do not leach harmful chemicals and comply with hygiene standards in North America, the UK, and France, respectively.
- CE Certification (EN 15874): This confirms compliance with European safety and performance standards.
- CCC Certification (GB 4806.7-2016): This ensures safety for drinking water contact in China.
- ASTM F2389: This is the primary U.S. standard for pressure-rated polypropylene piping systems.
- ISO 9001: This global standard for quality management systems indicates a manufacturer’s commitment to high-quality production processes.
Optimal Wall Thickness and Pressure Rating for PPR Pipe
The wall thickness of PPR pipe directly influences its pressure rating and long-term performance. Thicker walls are essential for applications involving higher pressures, preventing pipe bursting or leakage. For instance, high-rise buildings require pipes with greater wall thickness for safe and reliable operation due to elevated water pressure.
Appropriate wall thickness ensures long-term durability. It allows pipes to withstand internal and external forces, reducing the risk of cracks, leaks, and other failures. This, in turn, lowers maintenance and replacement costs. Correct wall thickness also contributes to optimal pipe performance by maintaining stable fluid flow rates and minimizing pressure loss.
The pressure rating (PN rating) of PPR pipes derives from the Hydrostatic Design Stress (HDS). HDS represents the maximum tensile stress the pipe material can continuously withstand for long-term durability, guaranteeing a 50-year service life.
The Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR) also directly correlates with pressure rating. SDR is the ratio of the pipe’s outside diameter to its minimum wall thickness. A lower SDR indicates a thicker wall relative to its diameter, resulting in a higher pressure rating. For example, an SDR 6 pipe has a significantly thicker wall and higher pressure capacity compared to an SDR 11 pipe of the same diameter.
For typical residential and commercial water supply applications, PPR pipes with an SDR 9 (or thicker) wall type are rated for 100 psi at 180ºF (690 kPa at 82ºC). These ratings meet the requirements of national model plumbing codes. Newer materials like PP-RCT offer approximately 25% higher pressure ratings than standard PP-R pipes for the same wall thickness and operating temperature.
Ensuring Heat Fusion Compatibility for Strong PPR Pipe Joints
Heat fusion forms the backbone of a robust PPR plumbing system. This process permanently joins PPR pipe and fittings, creating a homogeneous, leak-proof connection. Achieving optimal heat fusion compatibility requires precise control over several critical parameters.
Manufacturers design PPR pipe and fittings with consistent melting properties and uniform wall thickness. These characteristics ensure both components melt at the same rate and to the same depth during the fusion process. This consistency is vital for creating a strong, seamless bond. The fusion process itself demands correct temperature, correct pressure, and correct fusion time. For instance, the ideal temperature for welding PPR is typically around 260°C. Adhering to these parameters guarantees a molecular bond, making the joint as strong as the pipe itself.
Despite high-quality materials, poor installation practices often lead to system failures. These practices include improper cutting, misaligned joints, insufficient support, and poor fusion technique. Such errors may not be immediately apparent but can cause leaks over time. Several common issues arise from incorrect heat fusion techniques:
- Poor Pipe Cutting and Misalignment: Improper cutting creates uneven edges and misalignment. This results in weak connections and affects water flow.
- Incorrect Heating Time During Fusion Welding: Underheating causes incomplete fusion, leading to leaks and poor joint strength. Conversely, overheating can deform the pipe, creating blockages.
- Weak Joints Due to Improper Fusion Pressure: Insufficient pressure results in incomplete fusion. Excessive pressure can deform the fitting.
- Leaks Caused by Incorrect Pipe Insertion: Partial insertion creates weak connections that may fail under pressure.
Other critical factors also contribute to fusion failures:
- Incorrect Heating Temperature: Overheating causes over-melting, instability, deformation, or burning. Underheating leads to insufficient melting and insecure bonds, resulting in leakage.
- Inaccurate Heating Time: Excessive heating time can lead to over-melting, instability, cracks, or leaks. Insufficient heating time results in inadequate melting and loose joints.
- Misalignment of Pipe and Fitting: Incorrect alignment or uneven pressure during fusion can cause uneven melted areas. This compromises the seal and leads to loosening or leakage.
- Contaminated Pipe or Fitting Surface: Moisture prevents proper melting, increasing the risk of fusion failure. Oil and dirt impede heating, leading to uneven fusion and weak connections.
- Insufficient Cooling Time: Rapid cooling can cause cracks or deformation. Not allowing sufficient cooling time prevents the connection from setting properly, leading to leakage or instability.
Proper training and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for installers. These practices ensure the integrity of every PPR Pipe joint and the overall durability of the water supply system.
Types of PPR Pipe Fittings for Enhanced Durability
The specific types of PPR pipe fittings play a crucial role in building a robust and long-lasting water supply system. Each fitting serves a unique purpose, and its design directly impacts the system’s overall integrity and performance.
PPR Pipe Couplings and Connectors
PPR pipe couplings and connectors are fundamental components in any plumbing network. They primarily join two sections of PPR pipe, extending the pipeline or connecting different segments. Manufacturers design these fittings for a secure, leak-proof connection through heat fusion. This process creates a homogeneous bond, making the joint as strong as the pipe itself. High-quality couplings feature precise dimensions and smooth internal surfaces. These characteristics ensure minimal flow resistance and prevent pressure drops across the connection. Their robust construction and material purity contribute significantly to the system’s durability, allowing for reliable water transport over decades.
PPR Pipe Elbows and Bends
PPR pipe elbows and bends are essential for changing the direction of a pipeline. They allow installers to navigate corners and obstacles within a building’s structure. The design of these fittings significantly impacts water flow efficiency and system longevity.
- Smooth Inner Surface: These fittings feature a smooth inner surface. This design reduces friction, allowing water to flow freely and efficiently. It prevents increased energy consumption and lower water pressure.
- Resistance to Scaling: High-quality PPR elbows and bends resist the accumulation of scale and mineral deposits. This ensures consistent flow efficiency and pressure over time, especially in hard water areas.
- Low Friction Coefficient: The material’s low friction coefficient minimizes resistance to water flow. This leads to faster water delivery and prevents pressure loss throughout the system.
- Seamless Joints (Fusion Welding): Fusion welding creates strong, leak-free connections. These joints do not cause pressure loss, unlike threaded joints, ensuring a stable water pressure system.
Specific types of elbows offer different advantages:
- 45-degree PPR Elbow: This elbow is designed for smoother directional changes. It reduces turbulence and minimizes pressure loss. Its smooth inner surface further minimizes friction, ensuring efficient fluid flow. This design offers lower pressure loss and improved system efficiency compared to 90-degree elbows.
- 90-degree PPR Elbow: This fitting is suitable for tight spaces. While it can cause more water movement issues, specialized versions like the PPR Reducing Elbow minimize turbulence. It also has a smooth inner surface to reduce friction and prevent pressure loss, enhancing durability and heat resistance.
These design features ensure that PPR pipe elbows and bends contribute to reduced flow resistance and increased system longevity.
PPR Pipe Tees and Crosses
PPR pipe tees and crosses are crucial for distributing water flow within a system. Tees allow a single pipeline to branch into two separate directions, typically at a 90-degree angle. Crosses enable a pipeline to branch into three separate directions from a single point. Manufacturers design these fittings with precision to ensure balanced flow distribution and minimize turbulence at the branching points. Their robust construction, similar to other PPR fittings, ensures they withstand system pressure and temperature fluctuations without compromising integrity. The seamless heat fusion connections for these fittings prevent leaks and maintain consistent water pressure across all branches, making them vital for complex and durable water supply networks.
PPR Pipe Reducers and Adapters
PPR pipe reducers and adapters are essential for connecting pipes of different diameters within a water supply system. These fittings ensure a smooth transition in pipe size, which helps maintain consistent water pressure and flow rates throughout the network. Manufacturers design them for seamless integration through heat fusion, creating a strong, homogeneous joint that eliminates potential leak points. This process is crucial for the long-term durability of the plumbing system.
Reducers come in various forms, including concentric and eccentric types. Concentric reducers maintain the same center line for both pipe diameters, often used in vertical installations. Eccentric reducers offset the center lines, which helps prevent air pockets in horizontal lines. Adapters, on the other hand, connect PPR pipes to other types of piping materials or fixtures. They often feature threaded ends (male or female) for compatibility with metal components. The high-quality material of these PPR Pipe fittings ensures they resist corrosion and scaling, preserving their structural integrity and functionality over decades. Their precise manufacturing guarantees a tight fit and reliable performance, contributing significantly to a leak-free and efficient water distribution system.
PPR Pipe Valves and Manifolds
PPR pipe valves and manifolds provide critical control and distribution capabilities within a water supply system. Valves regulate or shut off water flow to specific sections, allowing for maintenance or isolation without affecting the entire system. Manifolds act as central distribution points, simplifying complex plumbing layouts and offering individual control over multiple outlets.
PPR valves, such as ball valves, gate valves, and check valves, offer superior performance compared to traditional metal alternatives. They feature corrosion-resistant bodies and internal components, ensuring smooth operation and preventing rust or mineral buildup that can impede flow. Heat fusion connects these valves directly into the PPR Pipe system, creating a permanent, leak-proof bond. This eliminates the common issue of leaks associated with threaded metal valves. Ball valves provide quick on/off control, while gate valves offer precise flow regulation. Check valves prevent backflow, protecting the water supply from contamination.
Manifolds streamline plumbing installations by consolidating multiple connections into a single unit. They distribute water from a main supply line to various fixtures or zones, often with individual shut-off valves for each outlet. This design simplifies troubleshooting and repairs, as technicians can isolate specific lines without disrupting the entire system. High-quality PPR manifolds are robust and resistant to pressure fluctuations, ensuring reliable water distribution. Their integrated design reduces the number of joints, further enhancing the overall durability and leak resistance of the water supply infrastructure.
Selection Criteria for Long-Lasting PPR Pipe Systems
Choosing the correct PPR pipe system requires careful consideration of several factors. These choices ensure durability and optimal performance for many years.
Application-Specific Requirements for PPR Pipe
Different applications demand specific PPR pipe characteristics. For instance, hot water recirculation systems have unique needs. The operating temperature should not exceed 140°F (60°C). Operating pressure must remain below 80 psi (551 kPa). Water velocity should not exceed 2 feet per second (0.6 m/s). PPR pipe fittings resist thermal expansion and contraction. This is crucial in hot water recirculation systems where water temperature constantly fluctuates. PPR’s low coefficient of thermal expansion allows it to adapt to dimensional changes without cracking or leaking. This ensures secure connections and reduces maintenance needs. Some PP-RCT pipes include a coextruded fiber layer. This layer minimizes expansion and contraction, especially with significant temperature differences. This fiber layer can reduce pipe expansion by up to 80% compared to non-fiber plastic pipes. Manufacturers must comply with various standards. These include ANSI/NSF 14, ANSI/NSF 61, ASTM F2389, and CSA B137.11. Other important certifications are ICC-ES-PMG 1106, ICC-LC1004, NSF/ANSI 51, and QAI P321-5.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings for PPR Pipe
Matching the pipe’s pressure and temperature ratings to the system’s demands is essential. Higher temperatures reduce the maximum allowable pressure. For example, a PN20 pipe handles its full 2.0 MPa pressure at 20°C. Its pressure rating drops to approximately 0.8 MPa when the temperature reaches 80°C. This relationship follows established derating curves in international standards. Most standard PPR pipe fittings handle hot water temperatures up to approximately 95°C. This makes them suitable for typical domestic heating systems and hot water supply. While they perform well at lower temperatures, continuous exposure to temperatures near the upper limit may gradually reduce their lifespan. For domestic water supply systems, a common pressure rating for PPR fittings is around 10-16 bars. This is sufficient for normal household water pressure. Higher-rated PPR fittings are available for industrial applications involving greater pressures.
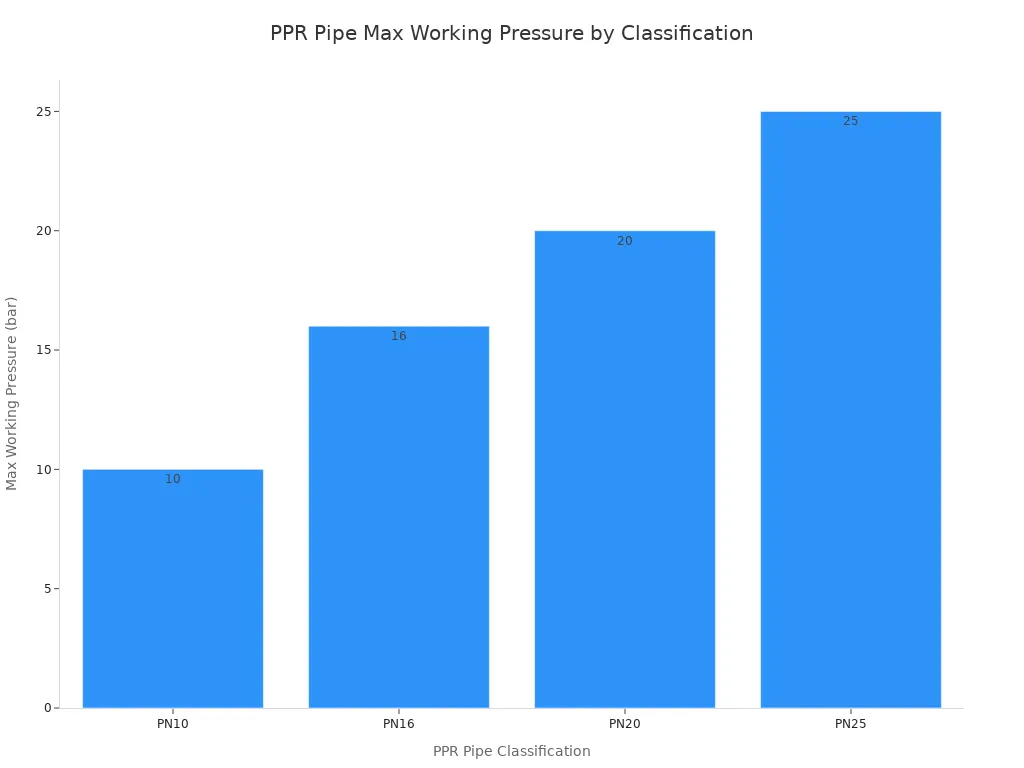
| Classification | Suitable for | Max Working Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| PN10 (1.0 MPa) | Cold water up to 20°C | 1.0 MPa (10 bar) |
| PN16 (1.6 MPa) | Hot water systems up to 60°C | 1.6 MPa (16 bar) |
| PN20 (2.0 MPa) | High-pressure applications, industrial hot water | 2.0 MPa (20 bar) |
| PN25 (2.5 MPa) | Heavy-duty industrial applications | 2.5 MPa (25 bar) |
Brand Reputation and Warranty for PPR Pipe Products
A reputable brand ensures product quality and reliable customer support. High-quality PPR fittings use pure polypropylene random copolymer. This material resists corrosion, scale buildup, and degradation. It adheres to international standards. Fittings must maintain integrity under both normal and high-pressure conditions. This prevents leaks or bursts. Fittings should handle temperatures from -10°C to 95°C without deforming, cracking, or leaching harmful substances. A well-designed fitting provides a secure, seamless connection to prevent leaks. Compliance with standards like ISO 9001 and NSF ensures safety and quality, especially for drinking water systems. Top PPR pipe brands provide excellent customer service. This indicates a strong focus on customer support.
Balancing Cost-Effectiveness with PPR Pipe Quality
Purchasers often weigh the initial cost of PPR pipe fittings against their long-term value. While PPR pipe fittings have higher initial material costs, they offer significant long-term benefits. For example, a 4-inch PPR pipe costs $3-6 per foot, compared to $2-4 for PVC. Installation also requires specialized heat fusion equipment, adding $200-500. It takes 15-20% longer. However, these upfront expenses are offset by long-term advantages. PPR’s superior joint strength leads to fewer callbacks and lower long-term labor costs. This contributes to a more economical outcome over a 20-year period despite the higher initial investment.
Over a 20-year period, PPR pipe fittings provide substantial long-term cost benefits. Their extended lifespan often exceeds 50 years, compared to PVC’s 25-40 years. This longevity reduces total ownership costs. PPR’s superior insulation properties also lead to reduced heating costs in hot water systems. Its better handling of temperature fluctuations results in fewer repairs and lower maintenance expenses. PVC, in contrast, may crack in extreme conditions.
Consider the long-term savings when comparing different piping systems:
| Cost Category | PVDF System | PVC System | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Materials | $10,000 | $3,000 | ($7,000) |
| Installation | $5,000 | $5,000 | $0 |
| Replacements | $0 | $15,000 | $15,000 |
| Maintenance | $2,000 | $12,000 | $10,000 |
| Downtime Costs | $1,000 | $25,000 | $24,000 |
| Total | $18,000 | $60,000 | $42,000 |
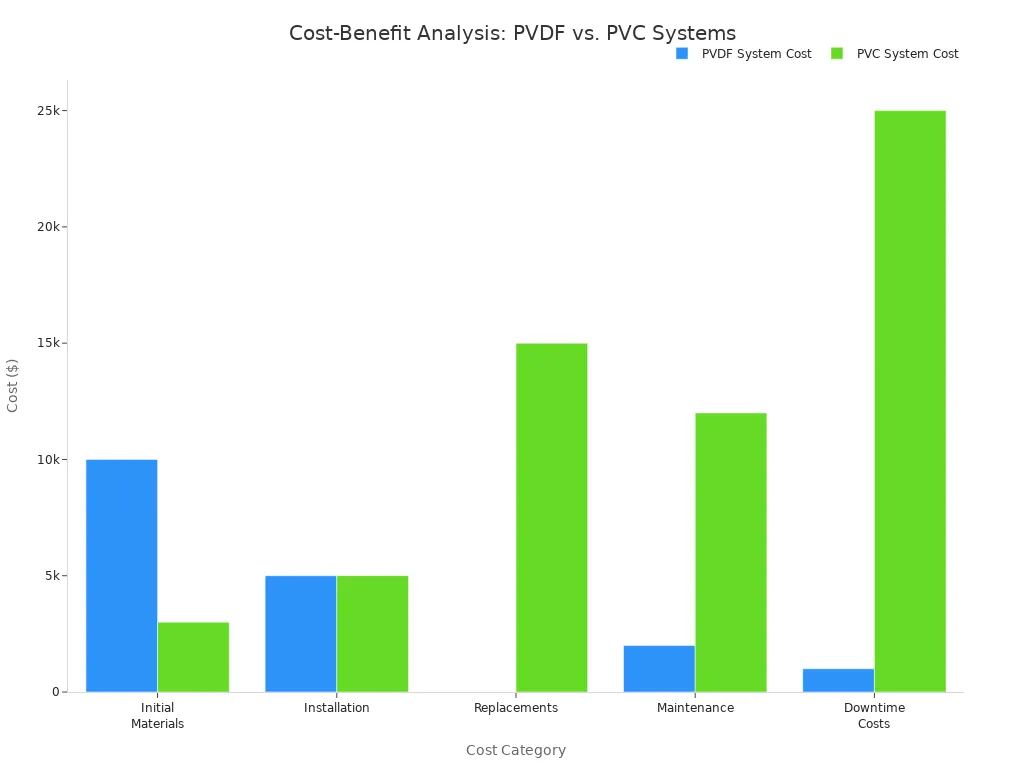
This comparison highlights the significant savings a high-quality system offers over its lifespan. Investing in premium PPR pipe fittings, like those from Donsen, ensures a durable water supply system. It also provides substantial cost savings in the long run.
Installation Best Practices for Maximum PPR Pipe Durability

Proper installation significantly impacts the longevity and reliability of a PPR water supply system. Adhering to best practices ensures maximum durability and prevents future issues.
Proper PPR Pipe Preparation
Thorough preparation of PPR pipes and fittings is the first critical step for strong, leak-proof joints. Installers must ensure clean and precise cuts.
- Preparation and Cutting: Measure and mark pipe lengths accurately. Use specialized PPR pipe cutters for perfect 90-degree, burr-free cuts. For pipes over 50mm, slight edge beveling may be needed.
- Cleaning and Degreasing: Thoroughly clean pipe ends and fitting sockets with isopropyl alcohol and lint-free cloths. This removes dust, grease, and moisture. This step is crucial to prevent joint failure.
- Marking Insertion Depth: Use depth gauges or markers to indicate the correct pipe penetration into fittings. This ensures proper insertion and prevents bottoming out.
Accurate Heat Fusion Techniques for PPR Pipe
Accurate heat fusion creates a homogeneous, permanent bond between PPR pipes and fittings. This technique requires precision and adherence to manufacturer guidelines. Installers must use the correct heating temperature, typically around 260°C, and maintain the specified heating and cooling times. Applying consistent pressure during the fusion process ensures a complete and secure weld. Proper alignment of the pipe and fitting prevents uneven melting and weak connections. These careful steps guarantee the joint becomes as strong as the pipe itself.
System Pressure Testing for PPR Pipe Integrity
After installation, a comprehensive pressure test verifies the system’s integrity. This crucial step identifies any potential leaks or weaknesses before operation.
The standard pressure testing procedure for newly installed PPR pipe systems, typically hydrostatic testing, involves several key steps:
- Pre-Test Preparations: Flush and clean the pipeline. Inspect all connections (fittings, joints, valves) for proper installation and tightness. Install test equipment (blind flanges, pressure gauges, relief valves, fill/drain points). Isolate the test section. Confirm test parameters like appropriate test pressure and medium.
- Filling the Pipe: Slowly fill the pipeline with clean water. Ensure air vents from high points.
- Pressurization: Gradually increase the pressure to 1.5 times the design working pressure, or as specified by relevant codes. For PPR pipes, the test pressure should be as per DIN 8077/8078.
- Stabilization: Allow the pressure to stabilize for 10-15 minutes before the official test begins.
- Holding Period: Maintain the test pressure for a duration of 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the applicable standard.
- Observation: During the holding period, monitor for any pressure drops. Visually check for leaks.
- Documentation: Record all relevant details. This includes test duration, initial and final pressure readings, temperature, and results of visual inspections.
- Test Result Evaluation: The test is successful if the pressure remains stable (within allowable drop limits). No visible leaks or damage occur. All test records are properly completed and signed off.
- Post-Test: Once the test successfully completes, slowly depressurize the system. Drain the water.
| Pipe Type | Typical Test Pressure |
|---|---|
| HDPE Pipe | 1.5 × Working Pressure |
| PVC Pipe | 1.25 × Working Pressure |
| Steel Pipe | ≥ 1.5 × Working Pressure |
| PPR Pipe | As per DIN 8077/8078 |
This rigorous testing confirms the system’s readiness for long-term, reliable service.
Avoiding Common PPR Pipe Installation Errors
Even with the highest quality PPR pipe fittings, installation errors can severely compromise a water supply system’s durability. Proper installation techniques are as crucial as the materials themselves. Installers must meticulously follow guidelines to prevent costly failures and ensure long-term reliability.
Several common mistakes frequently lead to system breakdowns:
- Improper Surface Preparation: Dirt, dust, oil, or moisture on pipe and fitting surfaces prevent proper bonding during fusion. This creates weak joints and leads to leaks.
- Incorrect Pipe Cutting and Deburring: Uneven or angled cuts create stress points and hinder proper insertion. Failing to deburr also leads to improper fusion and reduces water flow efficiency.
- Ignoring Thermal Expansion Allowances: PPR pipes expand and contract with temperature changes. Ignoring this crucial factor causes buckling, cracking, or stress at fittings.
- Incorrect Use of Fusion Tools: Using unsuitable or uncalibrated tools, applying uneven pressure, or using worn-out heating plates results in weak joints or surface damage.
- Poor Support and Pipe Anchoring: Unsupported or loosely anchored pipes sag. This creates stress at connection points and leads to cracking or separation over time.
- Neglecting Pressure Testing: Skipping pressure testing after installation means undetected leaks or defects can lead to costly water damage or system shutdowns later.
- Mixing Incompatible Materials: Improper connections between PPR and other materials like PVC, copper, or steel can cause thermal stress or galvanic corrosion. This significantly reduces the system’s lifespan.
- Ignoring Manufacturer Guidelines: Each PPR product has specific installation instructions. Ignoring these guidelines leads to performance issues because different materials require specific parameters.
- Improper Storage and Handling: Exposure to sunlight, dust, or sharp objects, or mishandling before installation, can deform or damage pipes. This compromises fusion quality.
Teams must prioritize training and strict adherence to established protocols. This proactive approach ensures every connection is secure and the entire system performs optimally for decades.
Maintenance and Longevity Tips for PPR Pipe Systems
Proper maintenance significantly extends the lifespan and ensures the consistent performance of PPR pipe systems. Adhering to best practices helps prevent premature failures and costly repairs. System owners must implement a proactive approach to maintain optimal functionality.
Regular System Inspections for PPR Pipe
Regular inspections are vital for guaranteeing the longevity and optimal performance of PPR pipe systems. These checks help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. A structured inspection schedule ensures comprehensive coverage.
| Maintenance Activity | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | 30 days |
| Pressure Testing | 6 months |
| Joint Examination | 12 months |
| Support Inspection | 12 months |
| System Performance | Continuous |

Key components of routine inspections include:
- Visual checks for wear or damage.
- Monitoring joint integrity.
- Assessing pipe alignment and stability.
- Verifying insulation effectiveness.
- Testing pressure levels.
System owners should conduct monthly visual inspections of the entire system. They look for signs of stress like whitening, deformation, or scratches. Installers perform detailed joint examinations quarterly. They check fusion connections for bead integrity, cracking, or distortion. Technicians conduct formal pressure tests every six months. They isolate sections and test at 1.5 times operating pressure for 30 minutes. Implementing continuous performance monitoring, using pressure gauges, and monitoring air quality and compressor cycle frequency also proves beneficial.
Preventing Mechanical Damage to PPR Pipe
Preventing mechanical damage to exposed PPR pipe sections is crucial for maintaining system integrity. Damage often occurs during storage, handling, or installation. Implementing careful strategies minimizes these risks.
To prevent mechanical damage to exposed PPR pipe sections, especially during storage and handling, effective strategies include:
- Careful Unloading: Use appropriate equipment like forklifts or cranes with slings. Lift pipe bundles without stress or bending. Avoid dropping or dragging pipes.
- Pre-Storage Inspection: Inspect pipes for any transit damage such as crushed ends or cracks before storing them.
- Proper Surface Preparation: Store pipes on a flat, level surface. Ensure the surface remains free from debris or sharp objects. These objects could puncture or deform the pipes.
- Horizontal Stacking: Stack pipes horizontally. Ensure layers are aligned and stable.
- Adequate Support Intervals: Utilize wooden beams or supports at regular intervals (e.g., 1 meter). This prevents sagging. Adjust intervals based on pipe diameter.
- Layer Separation: Place padding like cardboard or foam between pipe layers for extra protection. This is especially important for delicate surfaces.
- Stacking Height Limits: Adhere to a maximum stacking height (e.g., 1.5 meters). This prevents deformation of pipes at the bottom.
- Securing Stacks: Use straps or chocks to secure stacks against toppling. Avoid over-tightening.
- Careful Retrieval: Lift pipes carefully when retrieving them. Avoid pulling from the middle of a stack.
Understanding Chemical Compatibility with PPR Pipe
PPR pipes exhibit high resistance to many chemicals. However, certain aggressive substances can cause internal damage, leaks, or pipe failure if transported through them. It is crucial to ensure the PPR material is compatible with any chemicals being transported. For aggressive chemicals, consulting the manufacturer’s guidelines is advised to confirm compatibility. Chlorine is a substance that can degrade PPR pipe material over time. This potentially leads to pipe failures. This incompatibility often causes issues in plumbing systems, particularly when chlorine is used as a water treatment additive.
Addressing Leaks Promptly in PPR Pipe Systems
Promptly addressing leaks in PPR pipe systems is crucial for maintaining their durability and preventing significant damage. Even minor leaks can escalate quickly. They lead to extensive water damage and higher repair costs if left unaddressed. A proactive approach to leak detection and repair safeguards the entire water supply infrastructure.
System operators must address any detected leak immediately. This prevents further damage. Leaks can worsen over time. They lead to extensive water damage and higher repair costs. Maintaining a stock of spare parts and repair materials is also crucial. This allows for quick resolution of minor issues. It prevents delays in repairs.
Leaks in PPR systems often stem from improper installation, mechanical damage, or extreme temperature fluctuations. Visual inspections help identify early signs of leakage. These signs include damp spots, water stains, or visible drips around fittings and joints. A sudden drop in water pressure can also indicate a hidden leak within the system.
Ignoring small leaks has serious consequences. Water damage to surrounding structures can occur. Mold growth becomes a risk. The structural integrity of the building may compromise. Furthermore, unaddressed leaks lead to increased water bills. They also cause potential system failures.
A robust maintenance plan includes regular checks for leaks. It also ensures immediate action upon detection. This strategy minimizes downtime. It extends the operational life of the PPR piping system. It also protects the investment in a durable water supply.
Investing in high-quality PPR pipe fittings is paramount. This ensures a reliable and enduring water supply system. Careful selection, meticulous installation, and consistent maintenance significantly extend a plumbing system’s lifespan.
Durable PPR pipe fittings provide peace of mind. They also offer long-term savings and a consistently performing water supply.
Donsen’s certified products exemplify this commitment to quality.
FAQ
How long do durable PPR pipe fittings typically last?
High-quality PPR pipe fittings, made from pure PP-R material, can last over 50 years. Proper installation and adherence to operating conditions ensure this extended lifespan. They resist corrosion and chemical degradation, contributing to long-term reliability.
Why are international certifications important for PPR pipe fittings?
Certifications like CE, NSF, and WRAS guarantee product quality, safety, and performance. They confirm fittings meet strict international standards for material purity, pressure resistance, and hygiene. These certifications ensure suitability for potable water systems.
Which PPR pipe fittings are best for hot water supply systems?
PPR pipe fittings rated PN20 or PN25 are ideal for hot water systems. These fittings have thicker walls and higher pressure ratings. They safely handle continuous temperatures up to 95°C. This ensures durability and prevents deformation under heat.
How can one identify high-quality PPR pipe fittings?
Look for fittings from reputable manufacturers with clear markings of material grade (e.g., PP-R 80), pressure rating (PN), and relevant certifications. High-quality fittings have smooth surfaces, consistent wall thickness, and precise dimensions.
See Also
Dishwasher Safety: Can Your Air Fryer Basket Handle the Wash?
Best Air Fryer Alternatives Beyond BrandsMart for Your Kitchen 2024
Essential Accessories to Elevate Your Air Fryer Pan Experience
Top 5 Industrial Air Fryers for High-Volume Commercial Kitchens