How to Choose PPR Pipes and Fittings for Your 2026 Plumbing Needs
Selecting the right PPR pipes and fittings is crucial for reliable hot and cold water systems. You ensure long-term durability and efficiency in your plumbing for 2026 with informed decisions. PPR offers significant benefits for modern plumbing applications. Unlike metal fittings, PPR resists corrosion and scale buildup, preventing deterioration and maintaining efficiency. This material is also non-toxic, ensuring water quality, and recyclable, contributing to green building certifications. A reputable PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer provides these high-quality solutions. For a robust PP R piping system for hot water, choose products from an ISO/CE certified PPR pipe factory. When you need PPR fittings wholesale, find a trusted PPR plumbing system supplier.
Key Takeaways
- PPR pipes are good for hot and cold water. They last a long time. They do not rust.
- Choose PPR pipes with good quality. Look for certifications like ISO. Match pipe sizes correctly.
- Install PPR pipes with care. Use the right tools. Follow heating times for strong joints.
- PPR systems need little care. They are good for the environment. They save energy.
Understanding PPR for Modern Hot and Cold Water Systems

What are PPR Pipes and Fittings?
PPR pipes and fittings are essential components in modern plumbing systems. You use them for both hot and cold water distribution. These products primarily consist of Polypropylene Random Copolymer (PP-R). This material is a thermoplastic polymer. Manufacturers synthesize it through a copolymerization process. This process involves propylene monomers and a small amount of ethylene or another alpha-olefin comonomer. For distinctive colors, manufacturers add color masterbatch, which contains pigments and additives. Stabilizers and antioxidants are also included. These prevent degradation from UV radiation, oxidation, and environmental stress cracking.
Key Advantages of PPR Over Traditional Plumbing Materials
You gain significant benefits when choosing PPR over traditional plumbing materials like copper or PVC. Consider the cost savings; PPR pipes are typically 40-60% cheaper than copper. They also resist corrosion. Unlike copper, PPR is not affected by chlorine, salts, or acidic water. Copper, however, is prone to corrosion in aggressive water conditions. Installation is also easier with PPR. You can weld it quickly with a simple machine. Copper requires soldering or press-fit connections, which are more skill-intensive.
Compared to PVC, PPR offers superior temperature resistance. PPR pipes operate up to 95°C, making them ideal for hot water supply and central heating systems. PVC pipes typically have a maximum operating temperature of around 60°C. Exceeding this can lead to deformation. PPR also boasts greater durability and a lower risk of leaking. Its unique molecular composition and smooth outer surface prevent scale and mineral buildup. This is especially beneficial in regions with hard water.
How PPR Excels in Hot and Cold Water Applications
PPR truly excels in hot and cold water applications due to its robust properties. You can rely on PPR pipes to withstand temperatures up to 95°C (203°F) for hot water supply systems. They do this without significant degradation of their structural integrity. This high-temperature capability makes them a top choice for various uses. For high-pressure applications, including industrial hot water systems, you might select PN20 pipes, rated for 2.0 MPa (20 bar). Heavy-duty industrial applications often use PN25 pipes, rated for 2.5 MPa (25 bar). Even at 80°C, a PN20 pipe maintains a pressure rating of approximately 0.8 MPa. This ensures reliable performance under demanding conditions.
Essential Types of PPR Fittings and Their Specific Uses
Common PPR Pipe Types for Various Applications
You will find PPR pipes indispensable across many applications. They are crucial in residential plumbing systems, ensuring a safe and reliable water supply. PPR pipes are also employed in the food processing industry for distributing potable water and other liquids. This emphasizes hygiene and safety. The non-toxic nature of PPR material makes it safe for transporting potable water. You also use PPR pipes widely in healthcare facilities like hospitals and clinics for delivering potable water due to their hygienic properties. For radiant heating systems, you should consider PPR Type 3 (PP-R / PP-R80 – Polypropylene Random Copolymer). This is the most advanced PPR material. It offers an ideal balance of strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance. PPR Type 3 features high pressure and temperature resistance, suitability for both cold and hot water, and a long lifespan exceeding 50 years. Its non-toxic properties and fusion-weldable joints make it best suited for radiant floor heating systems.
Crucial PPR Coupling Fittings for Secure Connections
You need reliable connections in any plumbing system. A PPR coupling, also known as a socket, is a fitting specifically designed to connect two pipes of the same diameter. These couplings come in various sizes. They are suitable for both hot and cold water systems. You will find them easy to install. They also offer resistance to high pressure and temperature.
PPR Elbows and Tees for Efficient Directional Changes
You often need to change the direction of your piping. PPR elbow fittings allow you to do this efficiently. PPRC 45-Degree Elbows change the direction of fluid flow by 45 degrees. This allows for smooth and gradual redirection. These fittings feature a smooth socket at each end for PPR pipes. A central section curves at a 45° angle. They are versatile for residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing. You install them using heat fusion. For sharper turns, you use 90-Degree PPR Elbows. These connect two sections of PPR pipes at a sharp right angle. They are ideal for situations requiring abrupt directional changes, especially in tight spaces. Both types offer excellent durability, heat, and corrosion resistance. Their smooth inner surface ensures efficient fluid flow. Tees allow you to branch off a main line, creating a three-way connection.
PPR Reducers and Adapters for System Compatibility
You often need to connect pipes of different diameters within your plumbing system. PPR reducers and adapters provide the perfect solution for this. Reducing couplings, for example, join two pipes of varying sizes. They are essential for extending piping systems or repairing broken sections. These couplings include regular couplings, reducing couplings, and female/male threaded couplings. Specifically, reducing couplings enable the connection of pipes with different diameters.
You can see how different fittings manage size transitions:
| Fitting Type | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing Coupling | Joins pipes of different diameters (e.g., DN25 to DN20) | Tapered internal profile for smooth flow |
| Reducing Tee | Splits flow into outlets of varying diameters (e.g., DN25 main to DN20/DN15 branches) | Asymmetric internal geometry for size transitions |
| Reducing Bushing | Adapts male threads to smaller female threads (e.g., G1/2 male to G3/8 female) | Step-down adapter for retrofitting scenarios |
Reducing tees allow you to branch off a main line into smaller diameter pipes. Reducing bushings adapt male threads to smaller female threads. This helps you integrate new components into existing systems. These fittings ensure system compatibility and maintain efficient flow.
PPR Valves for Precise Flow Control
You need precise control over water flow in your plumbing system. PPR valves offer various solutions for this.
- PPR Ball Valves: These valves use a spherical disc to control water flow. They are known for quick shut-off and reliable performance. You turn a handle to rotate the ball, allowing or blocking water flow.
- PPR Gate Valves: You use a gate or wedge to control fluid flow with these valves. They typically operate in fully open or fully closed positions.
- PPR Check Valves: These valves allow fluid to flow in only one direction. They prevent backflow and protect equipment from reverse flow damage. They use a swing or spring mechanism that closes if flow reverses.
- PPR Pressure Reducing Valves: You maintain a consistent downstream pressure with these valves. They work despite upstream fluctuations.
- PPR Stop Valves (or Shut-Off Valves): Similar to ball valves, these often control flow to specific fixtures. They use a compression mechanism where a washer lowers onto a seat to stop water.
- PPR Butterfly Valves: These valves utilize a rotating disc for flow control. A quarter-turn of the handle positions the disc. They are compact and lightweight, excellent for regulating flow in larger pipes.
You select the right valve type based on your specific control needs.
Your 2026 Buyer’s Guide: Selecting Quality PPR Pipes and Fittings
You need to make informed decisions when selecting PPR pipes and fittings for your plumbing projects. This guide helps you choose high-quality products that ensure durability and efficiency for years to come.
Assessing Material Quality and Purity for Longevity
You must prioritize material quality and purity to ensure your PPR plumbing system lasts. High-quality PPR pipes and fittings offer exceptional longevity. They resist degradation over time. You should look for pipes made from 100% Type-3 random copolymer polypropylene (PP-R 80 or PP-RCT). This specific material composition provides superior performance. Virgin-grade PPR material is also essential. It guarantees consistency and durability. You avoid impurities that could compromise the system’s integrity.
Standards like DIN 8077/8078 and ISO 15874 provide guidelines for material quality. These standards ensure the raw materials meet strict requirements. Choosing products that adhere to these specifications gives you confidence in their long-term performance.
Understanding Pressure Ratings and Wall Thickness Requirements
You need to understand pressure ratings and wall thickness to select the correct PPR pipes. These factors directly impact your system’s ability to handle water pressure. PPR pipes come with different pressure nominal (PN) ratings. Each rating indicates the maximum pressure the pipe can safely withstand.
- PN10: This rating means the pipe handles a maximum pressure of 10 bars. You use PN10 pipes for low-pressure applications.
- PN16: These pipes are rated for a maximum pressure of 16 bars. You commonly use them for residential water supply systems.
- PN20: You select PN20 pipes for more demanding applications. They withstand a maximum pressure of 20 bars.
- PN25: These pipes handle a maximum pressure of 25 bars. You often use them for residential hot and cold water systems.
The wall thickness of PPR pipes directly affects their pressure rating. Pipes with thicker walls generally offer higher resistance to pressure. You match the PN rating to your specific application’s pressure demands. This ensures safety and prevents system failure.
Checking for Industry Certifications and Standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM)
You must verify industry certifications and standards when purchasing PPR pipes and fittings. These certifications guarantee product quality and compliance with international benchmarks. Look for products that meet standards such as:
- ISO 15874 series
- EN 15874
- ASTM F2389
- DIN 8077/8078
- GB/T 18742
- NBR 15884
ISO 15874 is a crucial standard for PPR piping systems. It specifies requirements for pipes made from polypropylene (PP) used in hot and cold water installations. This includes systems for drinking water and heating. ISO 15874-2:2013 outlines specific requirements for PP pipes. It covers various service conditions, design pressures, and pipe dimension classes. This standard also details test parameters for evaluation methods.
ISO 15874 certification involves several strict requirements:
- Raw Material Selection: You find only virgin polypropylene random copolymer (Type 3 or PP-R) acceptable. It must have specific melt flow rates, density, and resistance properties. Materials must also comply with certifications like NSF and WRAS.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Manufacturers enforce strict tolerances for internal/external diameters, wall thickness, and curvature. This ensures tight fits and secure welds.
- Thermal Stability and Pressure Testing: Fittings must withstand hydrostatic pressure tests at elevated temperatures. For example, they must endure 1.6 MPa at 95°C for 1,000 hours without leaking or deforming.
- Joint Integrity and Welding Compatibility: Fittings must show uniform melting behavior for complete bonding during socket fusion welding. Weldability testing validates this.
- Mechanical Strength and Impact Resistance: Products undergo testing under controlled conditions (e.g., ISO 9854 standards). This verifies impact resistance and tensile strength.
- Environmental and Hygiene Standards: Compliance with standards like NSF/ANSI 61, WRAS, and ACS prevents harmful chemical leaching. It also ensures biofilm resistance for potable water systems.
- Certification, Marking, and Traceability: Certified fittings carry standardized codes. These codes include the manufacturer, size, pressure class, material type, and applicable standards for traceability. Manufacturers must also provide certificates of conformity.
- Third-Party Testing: Independent labs (e.g., TÜV, SGS, DVGW) audit manufacturers. They inspect materials and conduct random sample testing to verify compliance.
You also encounter ASTM F2389, another important standard. This specification covers materials, dimensions, and performance for pressure-rated polypropylene (PP) piping systems.
| Requirement Category | ASTM F2389 Specification |
|---|---|
| Primary Application | Water service only |
| Covered Aspects | Materials, dimensions, performance for pressure-rated polypropylene (PP) piping systems |
| Compressed Air Provisions | No specific testing protocols or provisions for compressed air applications |
| General Restriction | Designed, tested, and approved exclusively for liquid transport applications |
| Safety Implication for Air | Use in compressed air systems is considered a code violation and safety risk |
ASTM F2389 is designed, tested, and approved exclusively for liquid transport applications. You find no specific testing protocols or provisions for compressed air applications within this standard. Using PPR pipes in compressed air systems is a code violation and a safety risk. No legitimate certification bodies provide specific approvals for PPR pipes in compressed air applications. Certifications like NSF/ANSI 61, WRAS, and DVGW validate PPR safety exclusively for water applications. Reputable PPR manufacturers explicitly state their products are for water only. They prohibit use with compressed air. Product markings like UL Listing and CE Marking for PPR are based on water system standards, not gas containment capabilities.
Matching Pipe and Fitting Sizes for Optimal Performance
You must correctly match pipe and fitting sizes for optimal performance in your PPR plumbing system. The diameter of PPR pipes directly impacts water flow and pressure. Incorrect sizing can lead to reduced water pressure or inefficient delivery.
Standard PPR pipe and fitting sizes commonly include:
- 20mm
- 25mm
- 32mm
- 40mm
- 50mm
- 63mm
- 75mm
- 90mm
- 110mm
- 160mm
You will find 20mm, 25mm, and 32mm sizes most common for residential applications. The pipe diameter is crucial. It directly affects the water flow and pressure within the plumbing system. A larger diameter pipe allows for greater water volume and less pressure drop. Conversely, a smaller pipe restricts flow. Always consult plumbing codes and system design specifications. This ensures you select the appropriate size for your specific needs.
Considering Temperature Resistance for Specific Hot Water Needs
You must carefully consider temperature resistance, especially for hot water applications. PPR pipes excel in handling high temperatures. This makes them ideal for various hot water systems.
PPR pipes offer excellent thermal performance:
| Thermal Factor | PPR Performance |
|---|---|
| Continuous Max Temperature | 95°C |
PPR pipes (PN 2.5) can maintain approximately 8 bar working pressure at 70°C. They can also maintain 5-6 bar at 95°C. This demonstrates a predictable and reliable derating curve for hot water systems. It ensures consistent pressure maintenance.
You can expect continuous operation within a range of 0°C to 70°C. Short-term resistance extends up to 95°C. For demanding hot water systems, PN25 hot water pipes are an excellent choice. These pipes are designed to operate continuously for one year under 9.7 bars pressure and 95°C hot water. This high-performance capability ensures durability and reliability for your specific hot water needs.
Evaluating the Reputation of a PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer
You should thoroughly evaluate the reputation of a PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer. A reputable manufacturer ensures product quality, reliability, and compliance with international standards. This protects your investment and guarantees the longevity of your plumbing system.
Look for a PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer with a long history in the industry. For example, Donsen, established in 1996, has over 20 years of experience. This experience indicates a deep understanding of plastic pipeline production. A strong PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer will also offer a comprehensive product range. This includes various pipe types, fittings, and valves. This ensures you find all necessary components from a single, trusted source.
Check for international certifications. These include CE certification (European Union), NSF certification (USA), SABs certification (South Africa), GOST certification (Russia), WRAS certification (England), SIAA certification (Japan), and SKZ certification (Germany). These certifications confirm that the PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer adheres to stringent quality and safety standards. A manufacturer with a global presence and agents in many countries demonstrates widespread acceptance and trust in their products. This indicates a reliable and high-quality PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer.
Installation Best Practices for PPR Plumbing Systems

You ensure the longevity and reliability of your PPR plumbing system through proper installation. Following best practices for fusion welding, avoiding common errors, and using the right tools are crucial steps.
Proper Fusion Welding Techniques for Secure Joints
You create strong, leak-proof connections by mastering fusion welding. The recommended hot melt welding temperature for PP-R is 260°C ± 10°C. Temperatures below 255°C lead to weak welds. Temperatures above 270°C damage the material, reduce the pipe’s inner diameter, and cause embrittlement. Industry standards like ISO 15874 and ASTM F2389 suggest a fusing temperature of 260°C ± 5°C. You should use a digital fusion tool to monitor and maintain this temperature. Allow 10-15 minutes for the machine to reach the set temperature before starting. Heating times vary based on pipe diameter:
| Pipe Diameter (mm) | Minimum Heating Time (seconds) |
|---|---|
| 16 | 5 |
| 20 | 5 |
| 25 | 7 |
| 32 | 8 |
| 40 | 12 |
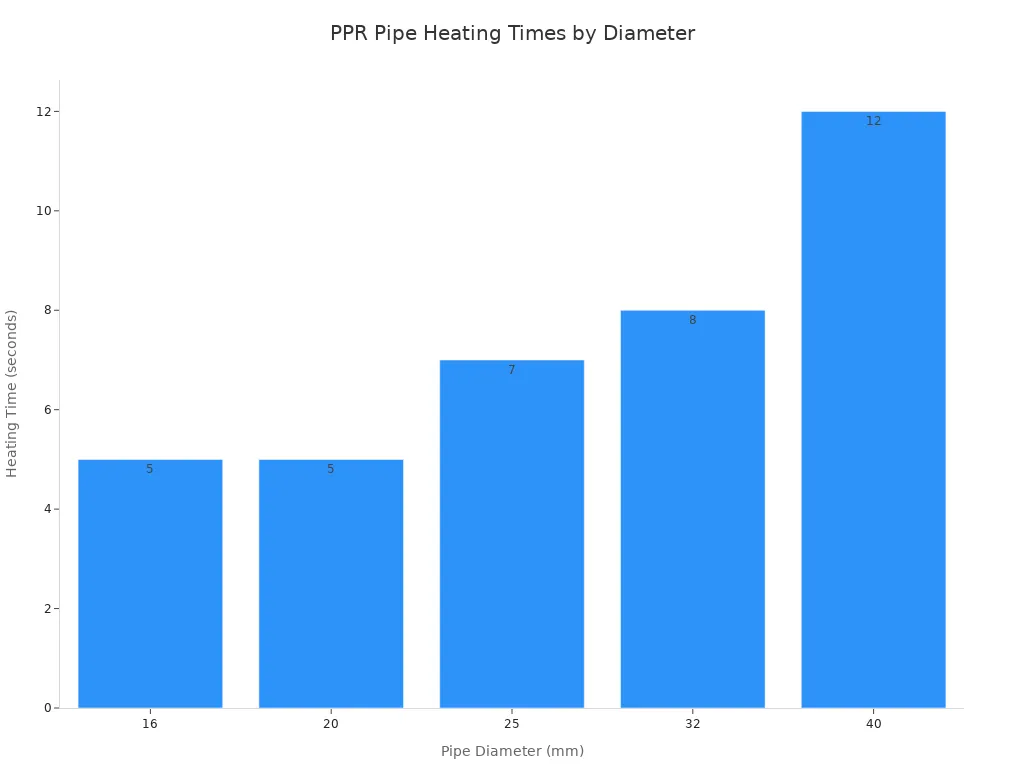
For instance, a 20mm pipe needs 5 seconds, while a 63mm pipe requires up to 20 seconds. Larger pipes, such as 110mm, can require up to 30 seconds of heating.
Avoiding Common Installation Mistakes
You prevent future problems by avoiding common installation mistakes.
- Overheating during fusion: This causes excessive softening of the inner surface. It leads to material deformation and restricts flow within the pipe.
- Underheating during fusion: This results in a weak molecular bond. The joint becomes prone to leakage or separation under pressure.
- Twisting or misalignment during fusion: Rotating or twisting the pipe while inserting it disrupts the molten layer. This leads to weak bonding or air pockets.
- Ignoring cooling time: Handling or pressurizing the joint too soon prevents the material from solidifying. This compromises the joint’s integrity.
- Poor alignment: Inaccurate alignment of pipes and fittings before fusion increases tension on joints. It causes uneven stress distribution.
Essential Tools for PPR Pipe and Fitting Installation
You need specific tools for proper PPR installation.
| Tool / Material | Purpose |
|---|---|
| PPR Fusion Welder | Heats pipes and fittings to melt and join them seamlessly, with temperature control for accuracy. |
| PPR Pipe Cutter | Ensures a perfectly straight cut, critical for a good seal. |
| Pipe Clamps (Metal) | Secures pipes firmly to walls or floors to prevent movement that could break joints. |
| Pressure Test Pump | Checks the completed system for any leaks, essential for verifying the installation. |
| Sandpaper & Clean Rag | Cleans burrs from cut ends and removes dirt or grease, which can ruin fusion bonds. |
| Marker/Paint Pen | Marks cutting lines and pipe routes on walls to avoid future damage during renovations. |
You also need a pipe reamer, measuring tape, and protective gloves and eyewear for safety. A deburring tool removes sharp edges after cutting.
Ensuring System Longevity Through Correct Installation
You guarantee the long-term performance of your PPR plumbing system through correct installation. Incorrect installation techniques compromise system integrity. For example, improper alignment, inadequate support, or insufficient anchoring create stress on joints. This leads to pipe movement or structural damage over time. You must follow best practices for installing PPR pipes. This maintains alignment, support, and anchoring throughout the system. Use appropriate tools and methods to secure pipes firmly in place. Avoid excessive bending or stretching during installation. Ensure fittings are correctly aligned and securely attached. This minimizes stress on joints. Utilize suggested fasteners and supports to ensure proper pipe alignment. This prevents sagging or shifting.
Proper support spacing is critical for preventing sag and maintaining system integrity. The required spacing varies based on water temperature and pipe type.
| Water Temperature | Standard SDR 11 | SDR 6 | Fiber-Reinforced |
|---|---|---|---|
| 68°F (20°C) | 3.9 ft (1.2 m) | 4.6 ft (1.4 m) | 5.2 ft (1.6 m) |
| 122°F (50°C) | 3.3 ft (1.0 m) | 3.9 ft (1.2 m) | 4.6 ft (1.4 m) |
| 176°F (80°C) | 2.6 ft (0.8 m) | 3.3 ft (1.0 m) | 3.9 ft (1.2 m) |
You can observe these recommendations visually:
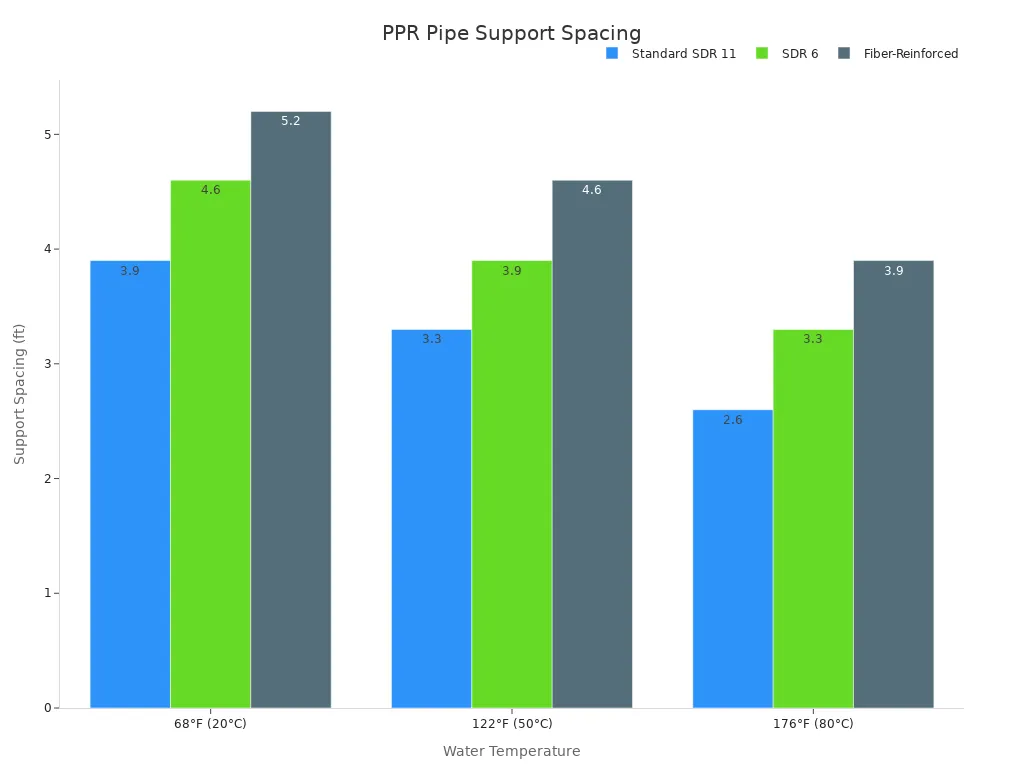
For 180°F water in a straight horizontal run, clip SDR 11 every 2.3 feet. Clip SDR 6 every 3.0 feet. Fiber-reinforced versions require clipping every 3.6 feet. Tighter spacing becomes necessary as heat softens the plastic. SDR 6 pipes have 70% thicker walls than SDR 11. This offers double the bending resistance. It allows for 30–40% wider clip spacing while maintaining the same sag limit.
You must use the correct clip type. Avoid bare metal straps; they can damage the pipe. Use plastic snap clips with soft rubber liners or insulated metal saddle clamps. These are specifically designed for thermoplastic pipes. Expansion compensation is crucial, even with frequent clipping. Install slide clips that allow 1/8-inch movement. Add U-bends or offset loops every 50–65 feet. This manages thermal expansion and prevents internal stress. Position a rigid clip within 4–6 inches on both sides of every valve, elbow, and tee. This dual support absorbs shock waves. It significantly reduces water hammer noise. Choose clips sized appropriately for the pipe diameter. For example, a 20 mm pipe needs 22–25 mm internal diameter clips. Map clip locations before cutting pipes. Plan a clip within 6 inches of every directional change. Use a laser line for long horizontal runs to ensure alignment. Anchor the line with fixed-point clips every 65 feet. This controls directional growth. Drill oversized holes through joists instead of notching structural members. Install clips loosely initially to allow thermal movement. After pressure testing, snug screws to 5 inch-pounds. Overtightening can crush the pipe.
Long-Term Benefits and Maintenance of PPR Systems
You invest in a plumbing solution that offers significant long-term advantages when you choose PPR pipes and fittings. These systems provide durability, require minimal upkeep, and contribute positively to environmental sustainability.
Expected Durability and Lifespan of PPR Plumbing
You can expect your properly installed PPR plumbing system to last for many decades. PPR pipes are designed to remain functional for 50 to 100 years under normal conditions. When you use them within recommended pressure and temperature limits, PPR pipes maintain their integrity for several decades. In residential applications, carrying cold or moderately hot water, PPR pipes typically offer a lifespan of around 50 to 70 years. This duration can vary based on the pipe’s quality, its environment, and how you use it.
Minimal Maintenance Requirements for PPR Systems
You will find PPR systems require minimal maintenance, even though they are highly durable. Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial for extending the lifespan of your pipes. You should conduct visual inspections regularly, looking for signs of damage like cracks or discoloration. Periodically, you can clean pipes to remove dust or dirt using mild detergents. You should also perform leak tests periodically, which can include pressure testing and monitoring for pressure drops. For commercial buildings, annual plumbing inspections ensure optimal condition.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of PPR
You contribute to a greener future when you choose PPR. PPR pipes are recyclable at the end of their service life, reducing landfill waste and supporting a circular economy. They remain stable and safe, and you can process and reuse them, reducing the need for virgin materials. PPR fittings use heat fusion for seamless, leak-proof joints, preventing water loss and waste. This is crucial for water conservation. PPR is highly resistant to chemicals, preventing corrosion and the leaching of contaminants into water. This maintains clean water. PPR pipes also offer superior thermal insulation compared to metal pipes. This reduces heat loss and improves energy efficiency in hot water supply systems. Their low thermal conductivity leads to improved energy efficiency, reduced heat loss, and cost savings for you.
You make a smart investment by carefully selecting your PPR pipes and fittings. Prioritize quality and compatibility for your 2026 plumbing needs. High-quality PPR fittings must match the chemical and thermal resistance of the pipes. This ensures system integrity. Always choose virgin PPR material for durability. Partner with a reputable PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer. They demonstrate commitment to quality through stringent processes and comprehensive testing. A reliable PPR pipes and fittings manufacturer also offers excellent customer service and a warranty. This provides peace of mind.
FAQ
What is the expected lifespan of a PPR plumbing system?
You can expect a PPR plumbing system to last 50 to 100 years. This longevity applies when you install it correctly and use it within recommended temperature and pressure limits. High-quality PPR ensures long-term durability.
Is PPR safe for drinking water applications?
Yes, PPR is safe for drinking water. Manufacturers produce it from non-toxic materials. It does not leach harmful chemicals into the water. Certifications like NSF and WRAS confirm its suitability for potable water systems.
What is the main advantage of PPR over traditional metal pipes?
PPR offers superior corrosion resistance. Unlike metal pipes, it does not rust or scale. This prevents water contamination and maintains consistent flow. You also benefit from easier installation and better thermal insulation.
Can you use PPR pipes for outdoor plumbing?
You can use PPR pipes outdoors. However, you must protect them from direct UV radiation. UV light can degrade the material over time. You should paint or cover exposed pipes to ensure their longevity.